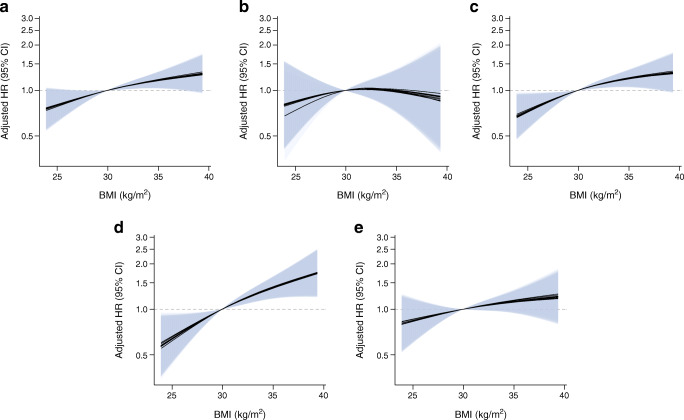
Fig. 1.
Association between pre-diagnosis BMI and risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes. (a) Total vascular complications. (b) Macrovascular complications. (c) Microvascular complications. (d) Kidney disease. (e) Neuropathy. Pre-diagnosis BMI was assessed as a continuous variable using restricted cubic spline regression, adjusted for age, sex, education, smoking status, smoking duration, physical activity, alcohol consumption, MedPyr score, family history of diabetes, myocardial infarction and stroke. Splines (black lines) and 95% CIs (blue shading) from ten imputation datasets are shown. Knot placement was 5th, 50th and 95th percentile. Median BMI of 29.9 kg/m2 served as reference. Test for non-linearity: total complications, p = 0.55; macrovascular complications, p = 0.64; microvascular complications, p = 0.36; kidney disease, p = 0.46; neuropathy, p = 0.86