Fig. 1.
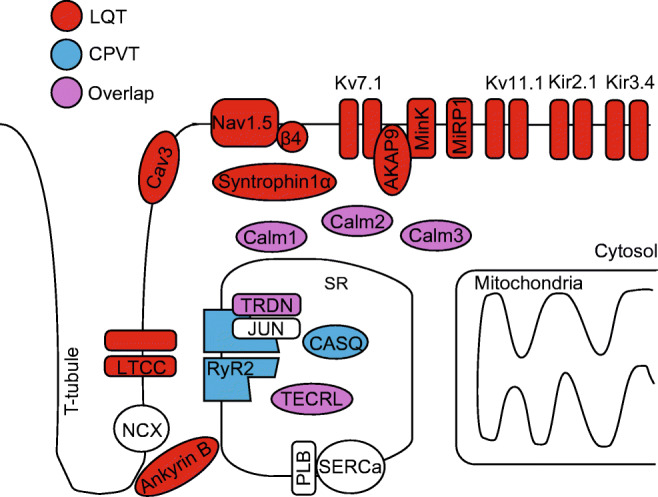
Proteins of cardiac excitation-contraction coupling associated with long QT syndrome or catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, caused by pathogenic mutation. Proteins with mutations associated with long QT syndrome are colored red; proteins with mutations associated with CPVT are colored blue; proteins with mutations that can cause long QT syndrome or CPVT are colored purple. Kv7.1; KCNQ1 gene, α-subunit of IKs channel, mutations underlie LQT1. Kv11.1; KCNH2 gene, α-subunit of IKr channel, mutation underlies LQT2. Nav1.5; SCN5a gene, α-subunit of INa channel, mutations underlie LQT3. Ankyrin B; ANK2 gene, functions as an adaptor protein, mutations underlie LQT4. minK; KCNE1 gene, β-subunit of IKs channel, mutations underlie LQT5. MiRP1; KCNE2 gene, β-subunit of IKr channel, mutations underlie LQT6. Kir2.1; KCNJ2 gene, α-subunit of IK1 channel, mutations underlie LQT7. LTCC; CACNA1C gene, mutations in α-subunit of ICa,L channel underlie LQT8 (Timothy syndrome). Cav3; CAV3 gene, caveolin-3 protein is a component of caveolae that co-localizes with Nav1.5, mutations underlie LQT9. β4; SCN4B gene, β-subunit of INa channel, mutation underlies LQT10. AKAP9; AKAP9 gene, protein mediates Kv7.1 phosphorylation, mutations underlie LQT11. Syntrophin1α; SNTA1 gene, protein regulates INa function, mutations underlie LQT12. Kir3.4; KCNJ5 gene, subunit of KACh channel, mutations underlie LQT13. Calm1; CALM1 gene, calmodulin serves as a Ca2+-binding messenger protein, mutations underlie LQT14 and CPVT4. Calm2; CALM2 gene, mutations underlie LQT15 and phenotype overlaps with CPVT. Calm3; CALM3 gene, mutations underlie LQT16 and CPVT6. TRDN; TRDN gene, triadin is an accessory protein of RyR2, mutations underlie LQT17, and phenotype overlaps with CPVT5. TECRL; TECRL gene, trans-2,3-enoyl-CoA reductase like protein belongs to the steroid 5-alpha reductase family, mutations underlie CPVT3 and LQT18. RyR2; RYR2 gene, ryanodine receptor is the major sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel, mutations underlie CPVT1. CASQ; CASQ2 gene, calsequestrin2 is an accessory protein of RyR2, mutations underlie CPVT2. JUN; ASPH gene, junctin is an accessory protein of RyR2, no CPVT or LQT-associated mutations reported. SERCa; ATP2A2 gene, protein functions as the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase, no CPVT or LQT-associated mutations reported. PLB; PLN gene, phospholamban functions as an inhibitory protein of SERCa, no CPVT or LQT-associated mutations reported
