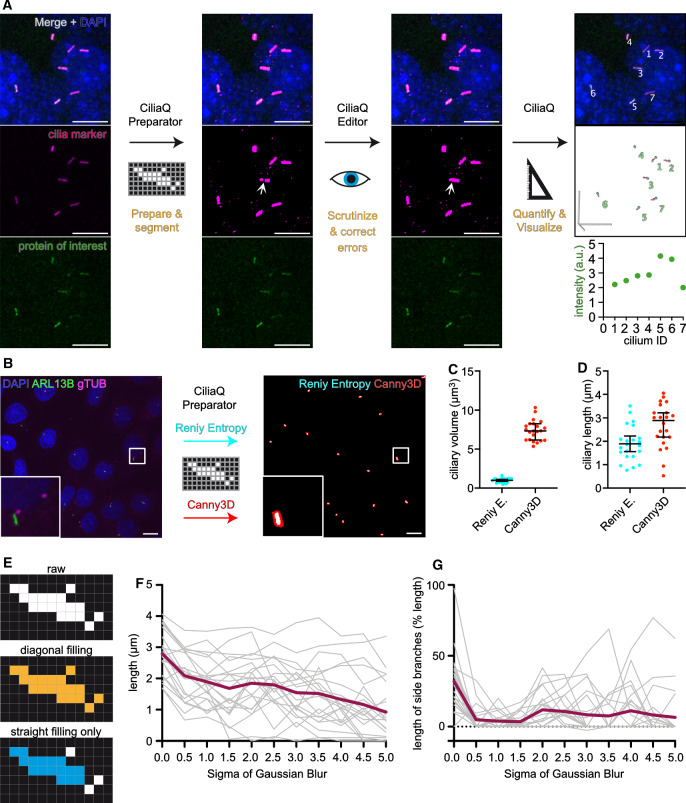
Fig. 1.
CiliaQ workflow. a CiliaQ constitutes a three-step workflow based on three ImageJ plugins: CiliaQ Preparator, which automatically segments the image into ciliary and background voxels, CiliaQ Editor, which allows manual correction of segmentation errors, and CiliaQ, which automatically reconstructs and quantifies all cilia in the image and outputs and visualizes the results. b–d Comparing segmentation with a single intensity threshold, determined by a histogram-based threshold method (Renyi Entropy), or with the Canny3D method in CiliaQ Preparator for processing an exemplary confocal stack image acquired from fixed, serum-deprived wild-type IMCD-3 cells, stained with DAPI to label nuclei (blue), an ARL13B antibody to label cilia (green), and a gamma-Tubulin antibody (gTUB) to label centrosomes (magenta). b Maximum projection of the original stack image (left) and the ARL13B channel after segmentation with CiliaQ Preparator using the Renyi-Entropy threshold (cyan) or the Canny3D method (red) (right). Magnified view on lower left. c Ciliary volume and d ciliary length determined by CiliaQ analysis of the segmented image stack shown in b using either the Renyi-Entropy-threshold- or the Canny3D-based segmentation for ciliary reconstruction. Each data point represents an individual cilium. All scale bars: . e Detecting objects in a pixelated binary image (top) with a Flood-Fill-Algorithm filling in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal direction (orange, center) or filling in horizontal and vertical direction only (blue, bottom). f, g Dependency of length quantification on the Gaussian blur applied (sigma in pixels) prior to skeletonization. f Length of the cilia presented in b (Renyi-Entropy threshold) determined by CiliaQ analysis with different Gaussian Blur sigma settings. g Total length of side branches appearing in the skeleton generated for measuring the ciliary length, presented as % length of the main branch