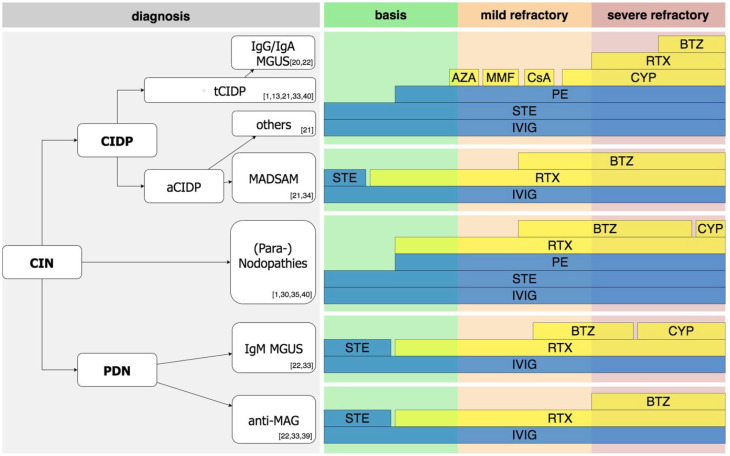
Figure 5.
Recommendation on therapeutic approaches in CIN. Note that the suggested algorithm is of evidence level III according to US Preventive Services Task Force. Due to the low number of patients in some subgroups, not only our own data from this manuscript but also recommendations from the literature are presented. Most important references are given in the figure. First, correct diagnosis according to the current diagnostic criteria needs to be made. As initial therapy, first-line therapy with STE, IVIG, or PE is recommended. If patients are refractory to these, early use of RTX is recommended in patients with MADSAM, (Para-) nodopathies, IgM MGUS, anti-MAG. In contrast, use of CYP prior to RTX is recommended in typical CIDP, patients with IgG or IgA MGUS, as well as atypical CIDP other than MADSAM and (Para-) nodopathies. In these, if course is rather mildly refractory, alternative immunosuppression, i.e., with AZA, MMF, or CsA is our recommendation. If RTX fails, BTZ should be considered. In rapid, severe refractory diseases, BTZ should be considered as add-on treatment after the first cycle of RTX.
aCIDP, atypical chronic inflammatory demyelination polyneuropathy; AZA, azathioprine; BTZ, Bortezomib; CIN, chronic immune-mediated sensorimotor neuropathies; CsA, cyclosporine A; CYP, Cyclophosphamide; IVIG, intravenous Immunoglobulins; MADSAM, Lewis-Sumner syndrome/multifocal acquired demyelinating sensory and motor; MAG, myelin-associated glycoprotein antibodies; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; PDN, paraproteinemic demyelinating neuropathy; PE, plasma exchange; RTX, Rituximab; STE, steroids; tCIDP, typical chronic inflammatory demyelination polyneuropathy; US, United States.