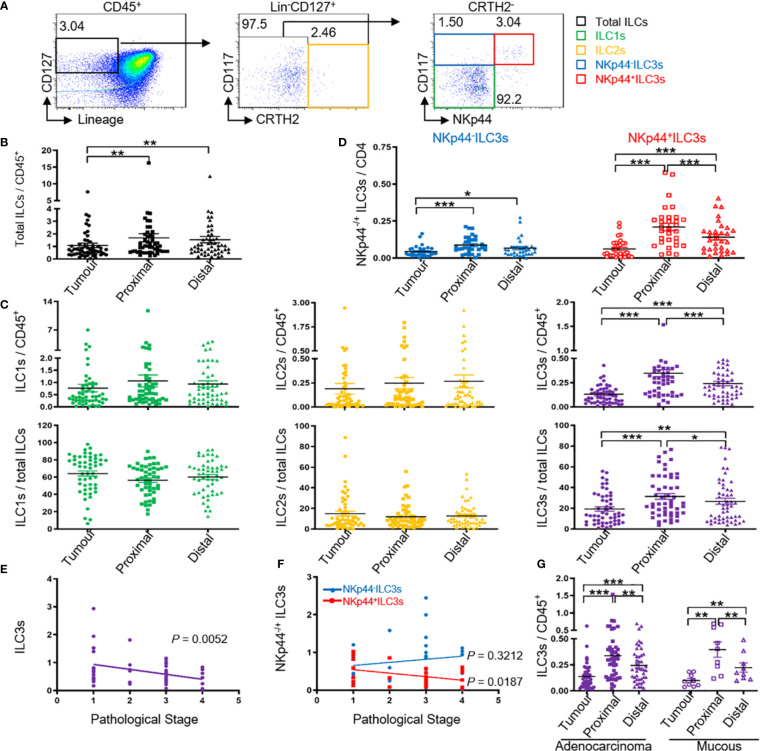
Figure 1.
Tumor ILC3s, especially NKp44+ ILC3s are negatively correlated with pathological stage. Distribution of ILCs and ILC subtypes by FACS. MNCs from tumor, proximal, and distal regions of 58 patients with colon cancer were prepared. (A) The gating used to define ILC subtypes: MNCs were stained for Lin cocktail (CD3, CD14, CD19, and CD20), CD94, CD34, CD1a, TCRα/β, TCRγ/δ, CD45, CD127, CRTH2, and CD117. Total ILCs were identified as Lin− CD94− CD34− CD1a− TCRα/β− TCRγ/δ− CD45+ CD127+, ILC1s were identified as Lin− CD94− CD34− CD1a− TCRα/β− TCRγ/δ− CD45+ CD127+ CRTH2− CD117−, ILC2s were identified as Lin− CD94− CD34− CD1a− TCRα/β− TCRγ/δ− CD45+ CD127+ CRTH2+, and ILC3s were identified as Lin− CD94− CD34− CD1a− TCRα/β− TCRγ/δ− CD45+ CD127+ CRTH2− CD117+. ILC3s were further divided into NKp44+/− ILC3s. (B) ILC levels among the CD45+ cells in the indicated tissues. (C) Percentage of ILC1s, ILC2s, and ILC3s among CD45+ cells and total ILCs in the indicated tissues. (D) Percentage of NKp44+/− ILC3s among CD45+ cells in the indicated tissues. (E, F) Correlation between the percentage of ILC3s or NKp44+/− ILC3s in tumor (T) versus distal (D) tissue and the pathological stage of cancer. The distal tissue was considered normal tissue and was used for normalization to the background, here T/D. (G) Percentage of ILC3s among CD45+ cells in colon glandular cancer and mucous carcinoma tissue. In (B–D, G), each symbol represents the indicated tissue from one patient (circle, tumor; square, proximal region; triangle, distal region). In (A, E, F), each dot represents one patient. A paired t-test and Spearman test were used for statistical comparison. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.