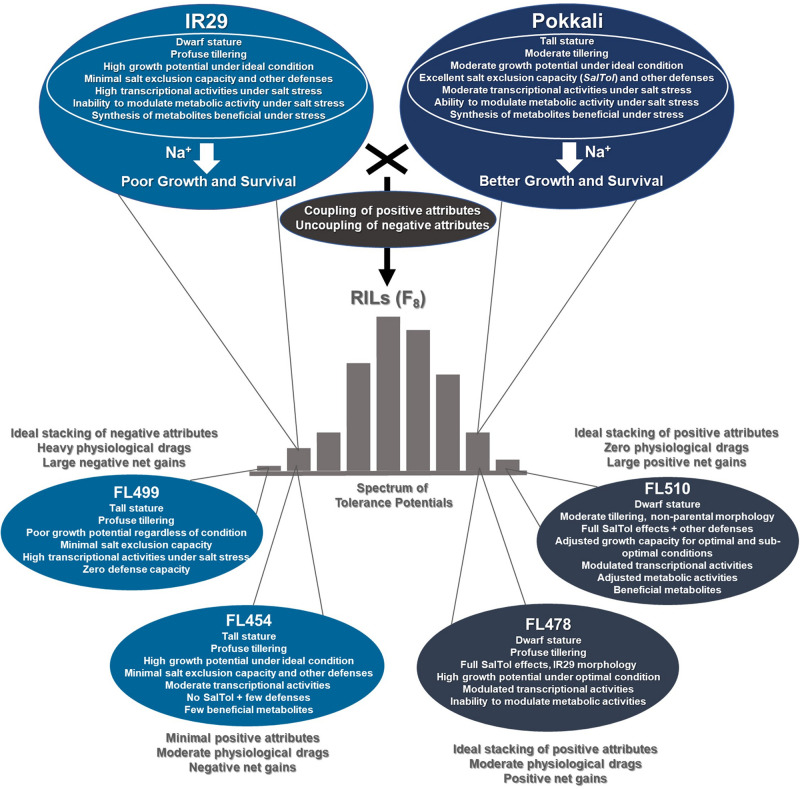
FIGURE 9.
Hypothetical model of physiological coupling and uncoupling in transgressive segregants for salinity tolerance across the IR29 × Pokkali recombinant inbred population based on macro-physiological, biochemical, and molecular profiles according to de los Reyes (2019). This model proposes that the novelties of FL510 and FL499 are due to the coupling in the progeny of the good properties coming from either parent or uncoupling of bad properties from the good properties from the same parent. On top of the core mechanisms that contribute to a large proportion of phenotypic variance for defense potentials, each parent has their own characteristics that may or may not be beneficial under stress. Benefit from IR29 would be its superior growth and development potentials. Pokkali offers many stress defense mechanisms including salt exclusion. Combining the physiological potentials of parents with the reconfigured (non-parental) properties led to positive or negative coupling and uncoupling effects in RILs.