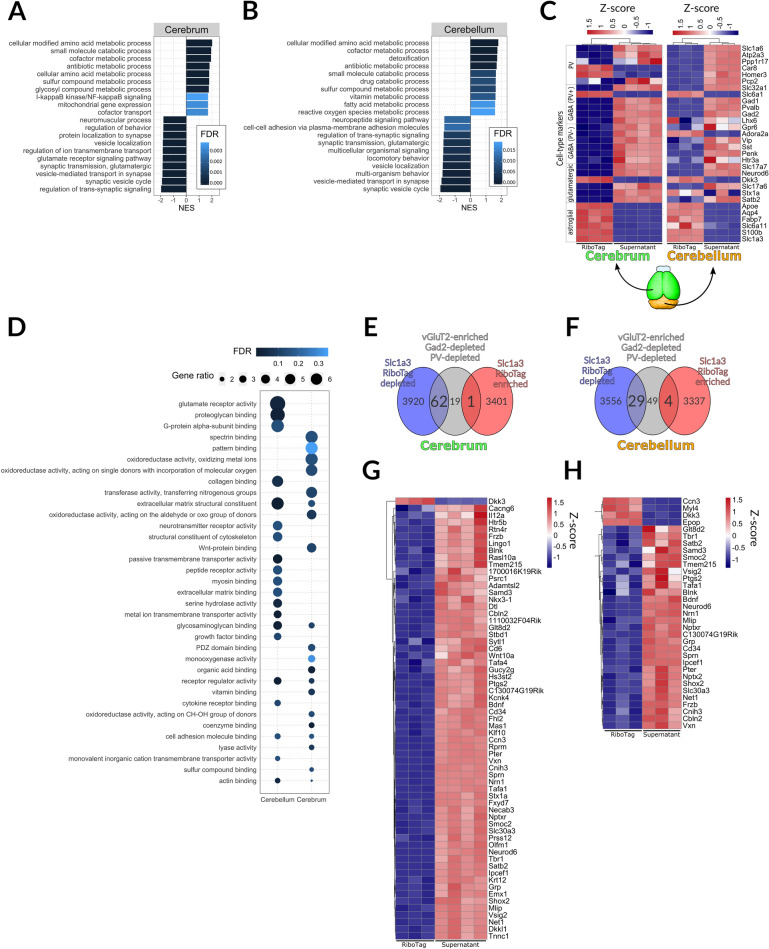
Figure 5.
Assessment of RiboTag analysis specificity. (A,B) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of RiboTag IP in cerebrum (A) and cerebellum (B); negatively and positively enriched genes correspond to gene sets functionally related to neuronal and glial function, respectively; analysis was done using WebGestalt105 using molecular function GO terms, genes were ranked as described in the methods section and top 10 hits for each region were shown; NES = normalized enrichment score. (C) Heatmap showing relative distribution of RiboTag RPKM values for genes for cell type-enriched mRNAs that we previously used to validate cell type specificity of gene expression in Tagger mice25. Each column represents one biological replicate. Z-score was calculated as follows: , where SD is standard deviation. (D) GO analysis of genes determined as enriched (FDR < 0.05, LFC > 1) in BG and AC; top 20 GO categories (molecular function, MF) for each cell population were shown. (E,F) Venn diagrams showing overlaps of significantly enriched (red circle, LFC > 1, FDR < 0.05) and depleted (blue circle, LFC < − 1, FDR < 0.05) genes in Slc1a3-2A-CreERT2::RiboTag with genes enriched in glutamatergic neurons in vGluT2-Cre::Tagger mice. Grey circle contains genes that are enriched in vGluT2 + cells (LFC > 1, FDR < 0.05), and simultaneously not enriched in PV + neurons and Gad + neurons (LFC < 0, FDR < 0.05 for both cell types). Note that in case of our Tagger analysis whole brain was used, hence the expected overlap (circle intersections; genes enriched in vGluT2 should be depleted in astroglia and vice versa) is more pronounced for the cerebrum (more similar to Tagger samples) (E) than for the cerebellum (F). (G,H) Heatmaps showing genes from the intersections of the Venn diagrams in E and F.