Figure 4.
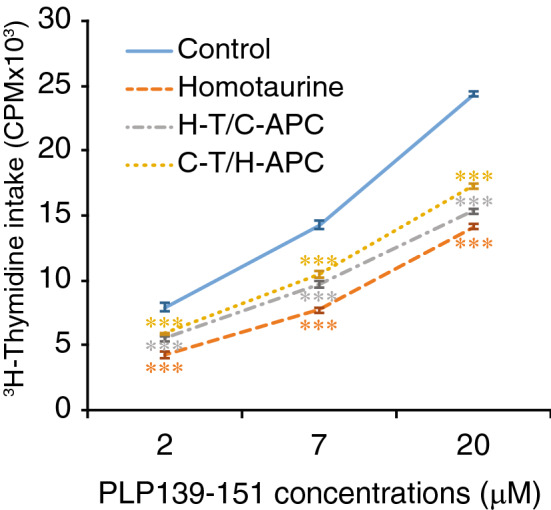
Homotaurine impairs the functions of splenic APCs. SJL mice were immunized with PLP139-151 and treated with, or without, homotaurine (0.25 mg/ml). Nine days later, CD4+ T cells were purified from their popliteal lymph nodes and T cell-depleted splenic mononuclear cells (APCs) were prepared by negative selection using microbeads and magnetic sorting. The T cells were mixed with APCs in a ratio of 5:1 and tested for T cell proliferation to the indicated concentrations of PLP139-151 for 3 days by 3H-thymidine incorporation. “Control” (solid blue line) represents 3H-thymidine incorporation by T cells and APCs isolated from untreated mice; “Homotaurine” (orange dashed line) shows 3H-thymidine incorporation by T cells and APCs isolated from homotaurine-treated mice; “H-T/C-APC” (grey dash/dotted line): T cells were isolated from homotaurine-treated mice and mixed with APCs from control untreated mice. “C-T/H-APC” (yellow dotted line): T cells were isolated from control mice and mixed with APCs from homotaurine-treated mice. Data are expressed as the mean values of each group ± SEM. The control cells without peptide stimulation had a CPM of 600–800 and the intra-group variation was less than 12%. N = six mice per group tested in two separate experiments. ***p < 0.001 vs. control by Student’s t-test.
