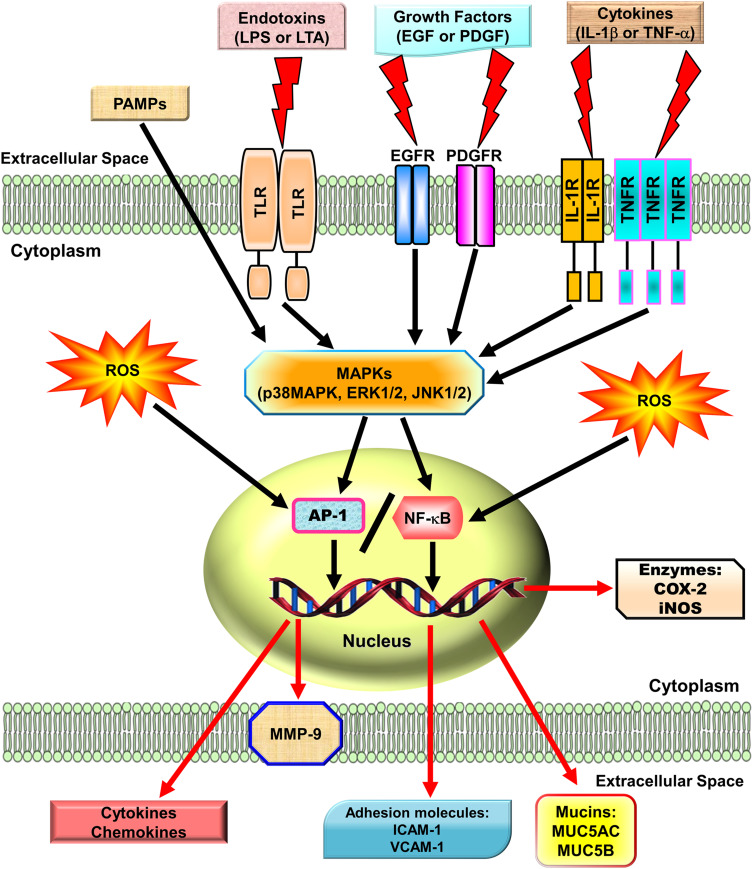
Figure 1.
The roles of ROS, pro-inflammatory mediators, and transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB in pulmonary inflammatory diseases. Pathogen-activated molecular patterns (PAMPs), including endotoxins (LPS or LTA), growth factors (EGF or PDGF), and cytokines (IL-1β or TNF-α), activate downstream pathways (p38 MAPK, JNK1/2, and ERK1/2) via their respective receptors (TLR, EGFR, DPGFR, IL-1R, and TNFR) to promote transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1 activities also activated by ROS, leading to genes transcription (including cytokines, chemokines, MMP-9, COX-2, iNOS, ICAM-1, VCAM-1, MUC5AC, and MUC5B) and pulmonary inflammation.
Abbreviations: LPS, lipopolysaccharides; LTA, lipoteichoic acid; EGF, epidermal growth factor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; TLR, Toll-like receptor; AP-1, activator protein 1; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinases-9, NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; ROS, reactive oxygen species; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule -1; MUC5AC, mucin 5AC; MUC5B, mucin 5B.