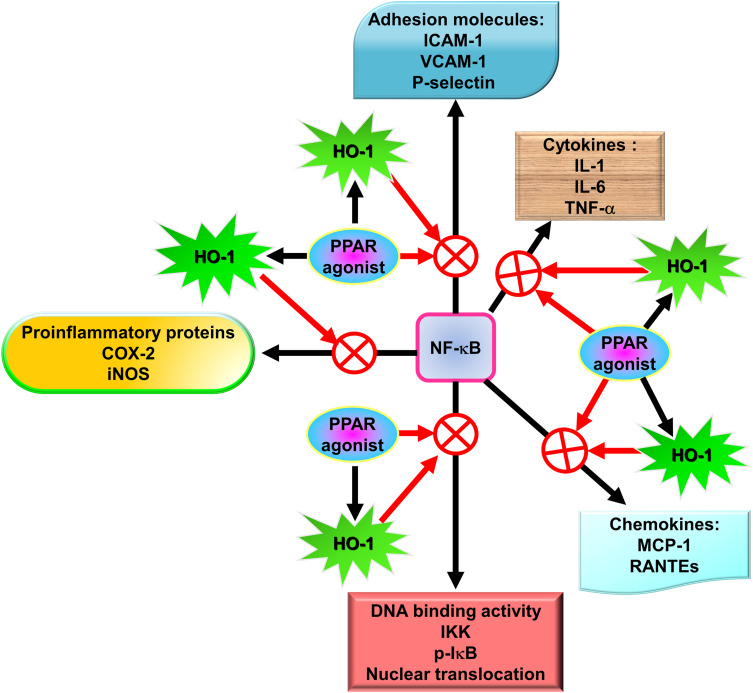
Figure 2.
The functions of PPARs agonists in pulmonary inflammation. PPARs agonists and PPARs agonist-induced HO-1 upregulation can inhibit NF-κB activity via blocking IKK activity and IκB phosphorylation, leading to suppression of NF-κB nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity and in turn reduction of gene expression including MCP-1, iNOS, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, P-selectin, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, and RANTEs.
Abbreviations: TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; HO, heme oxygenase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; RANTEs, regulated upon activation normal T-cell expressed and secreted; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; IKK, IκB kinase.