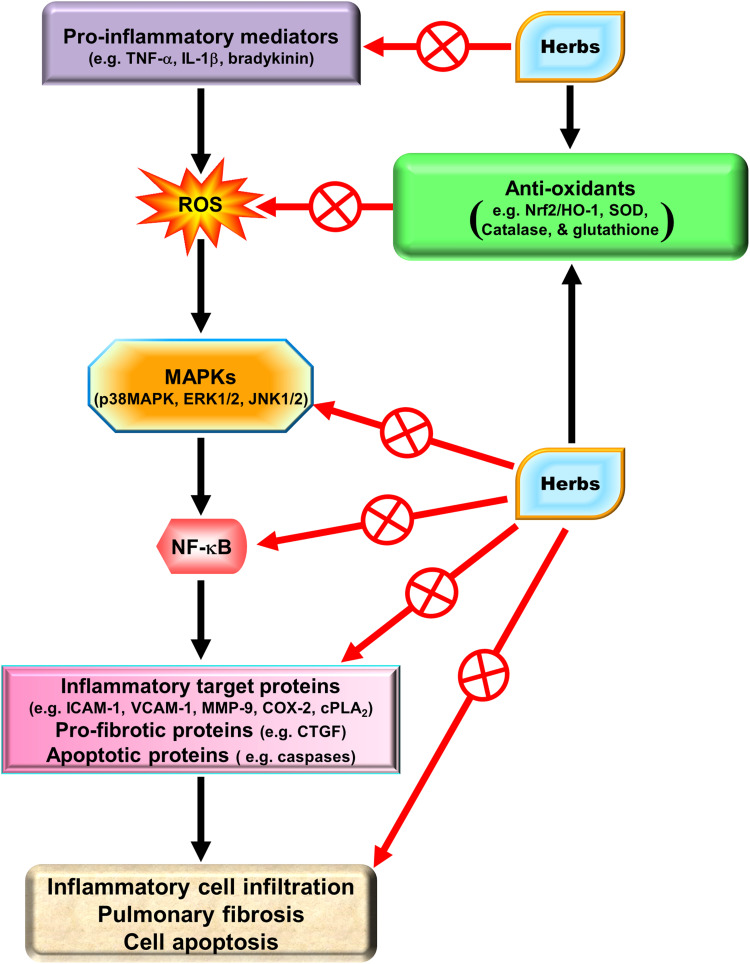
Figure 3.
The anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and anti-apoptotic mechanisms of Chinese herbs in the lungs. Herbs can target individual signal molecules including ROS, MAPKs, and NF-κB as well as pro-inflammatory mediators to block the expression of pro-inflammatory proteins, pro-fibrotic proteins, and pro-apoptotic proteins.
Abbreviations: COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; cPLA2, cytosolic phospholipase A2; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; HO, heme oxygenase; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; IL-1, interleukin-1; JNKs, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.