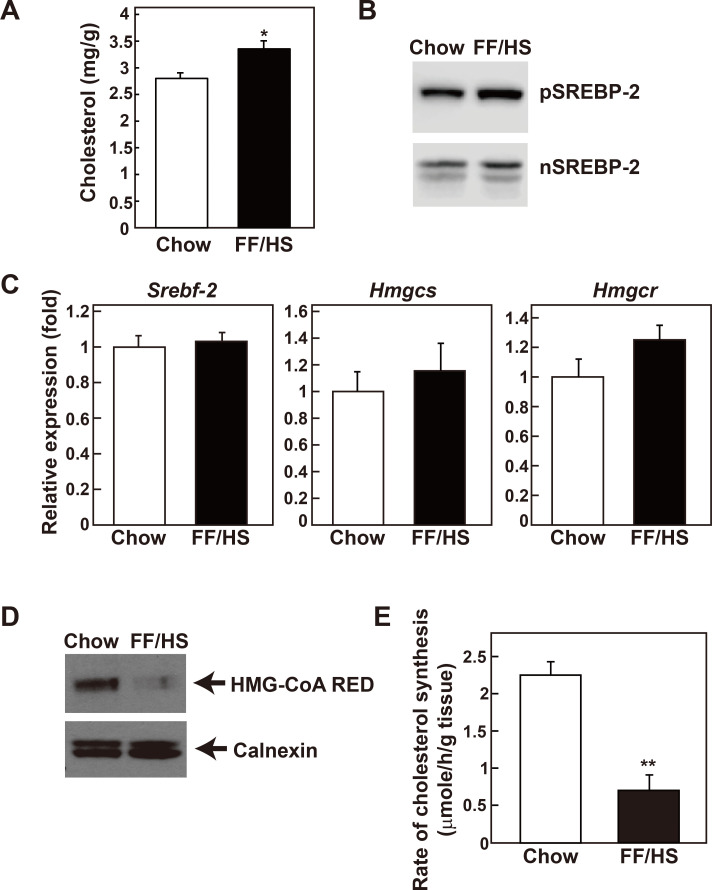
Fig. 2. Hepatic cholesterol content and synthesis rates in mice fed a chow or an FF/HS diet.
(A) Cholesterol contents were measured in the liver of mice fed a chow or an FF/HS diet for 20 days. Data represents the mean ± SE of 10 mice. (B) Membrane and nuclear proteins presented in Fig. 1 were used for immunoblot analysis of SREBP-2. (C) mRNA expression of genes involved in cholesterol synthesis were determined. Values represent the mean ± SE of 10 mice relative to mice fed a chow diet, which is defined as 1. Apoe was used as the invariant control. (D) Equal amounts of membrane proteins prepared individually from 6 mice of the same group were pooled and immunoblot analysis of HMG-CoA reductase was performed. Calnexin was used as a loading control. (E) In vivo synthesis rates of cholesterol were measured in livers of mice fed with a chow or an FF/HS diet. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with 3H-labeled water. One hour after the injection, the incorporation of 3H-labeled water into newly synthesized cholesterol was measured in the liver. Each bar represents the mean ± SE of the values from 5 mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test.