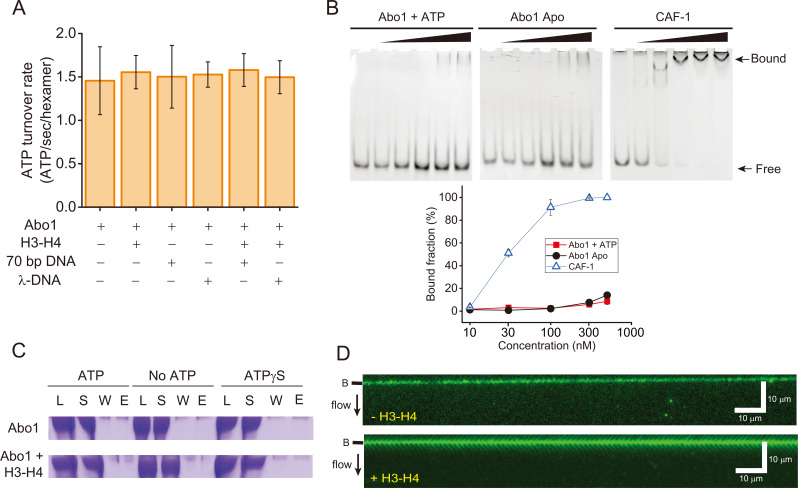
Fig. 3. Abo1 and DNA interactions.
(A) ATP hydrolysis activity of Abo1 in the presence of DNA (short 70 bp DNA and λ-DNA [48,502 bp]) and/or H3-H4 dimers. (B) EMSA for the DNA interactions with Abo1 and CAF-1. Abo1 or CAF-1 was incubated with 10 nM of 80 bp DNA at different concentrations (0, 10, 30, 100, 300, and 500 nM). (Top left) Abo1 and ATP. (Top middle) Abo1 Apo (without ATP). (Top right) CAF-1. (Bottom) Quantified bound fraction (%). Red square: Abo1 + ATP. Black circle: Abo1 Apo. Empty triangle: CAF-1. (C) Magnetic bead pull-down assay. Streptavidin-coated magnetic beads were conjugated with biotinylated 269 bp Widom 601 DNA. Abo1 alone or Abo and H3-H4 dimers were incubated with the magnetic beads with ATP, no ATP, or ATPγS. The load (L), supernatant (S), wash (W), and eluate (E) fractions were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. (D) DNA curtain image for Alexa488-labeled Abo1 in the presence of ATP, without H3-H4 dimers (top) and with H3-H4 dimers (bottom). No binding of Abo1 to DNA molecules was observed regardless of H3-H4 dimers. The black bar next to the image represents the nano-barrier position. The black arrow indicates flow direction.