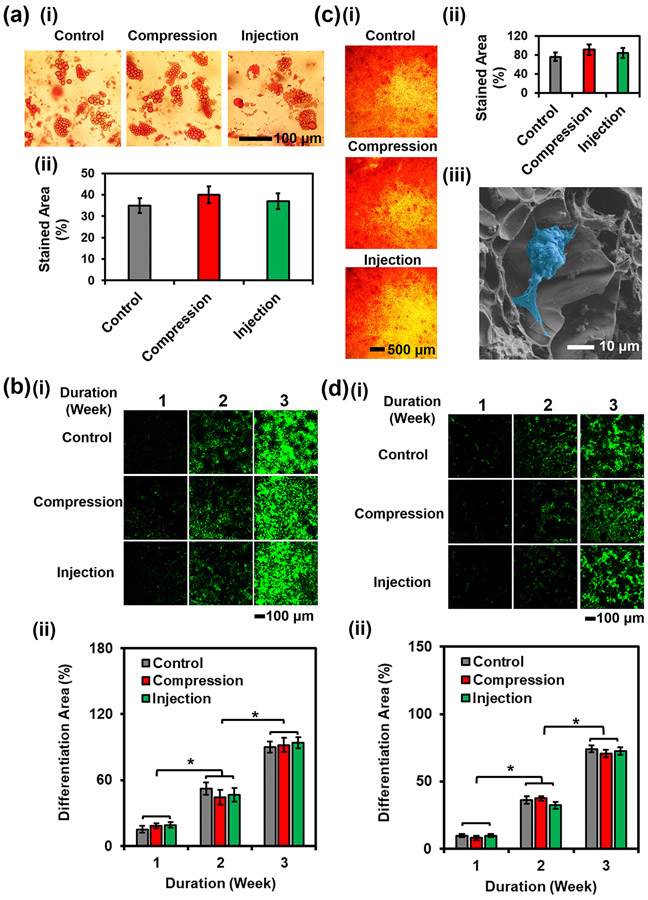
Figure 6.
Evaluation of hMSC differentiation within the 3D-bioprinted porous hydrogel constructs. (a) (i) Photographs and (ii) quantification of Oil Red O-stained hMSCs encapsulated in the 3D-bioprinted porous hydrogel constructs under different treatments at 3 weeks of adipogenesis. (b) (i) Fluorescence micrographs and (ii) semi-quantitative measurements of PPARγ immunostaining of hMSCs encapsulated in the 3D-bioprinted porous hydrogel constructs under different treatments over the course of 3 weeks of adipogenesis. (c) (i) Photographs and (ii) quantification of Alizarin Red S-stained hMSCs encapsulated in the 3D-bioprinted porous hydrogel constructs under different treatments at 3 weeks of osteogenesis. (iii) SEM micrograph of a differentiated cell (pseudo color in blue) and mineral deposition in the micro-nanoporous hydrogel at 3 weeks of osteogenesis. (d) (i) Fluorescence micrographs and (ii) semi-quantitative measurements of RUNX2 immunostaining of hMSCs encapsulated in the 3D-bioprinted porous hydrogel constructs under different treatments over the course of 3 weeks of osteogenesis (n=3, *p<0.05).