Figure 1.
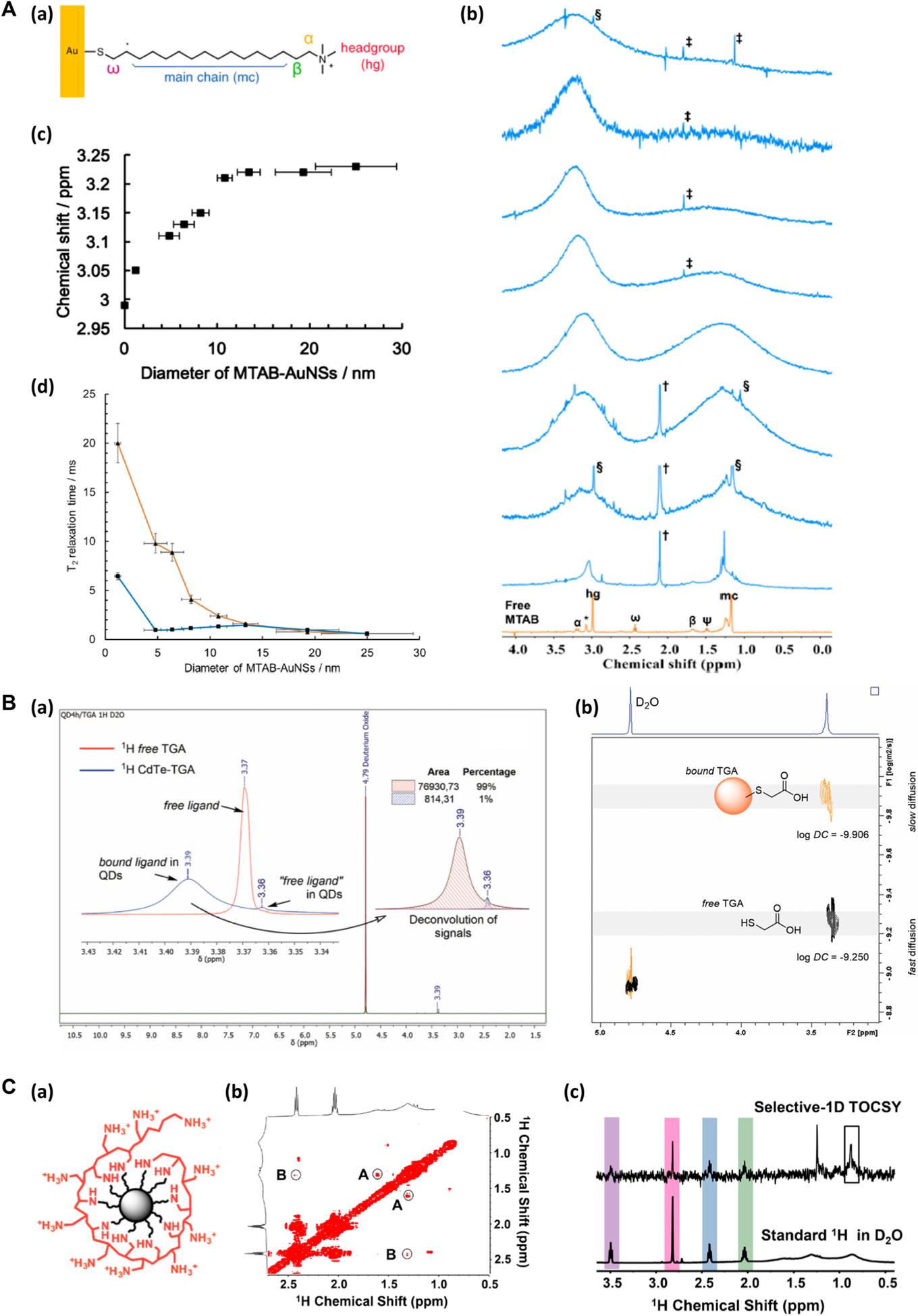
NMR in the analysis of nanomaterial surface functionalization. (A) (a) MTAB-functionalized AuNS. (b) 1H NMR spectra of free MTAB (orange) and MTAB-AuNSs (blue) in D2O. The blue traces from bottom to top corresponded to the particle size of 1.2 ± 0.3 nm, 4.8 ± 1.1 nm, 6.4 ± 1.1 nm, 8.2 ± 0.9 nm, 10.8 ± 0.8 nm, 13.4 ± 1.2 nm, 19.3 ± 3.0 nm, and 25.0 ± 4.4 nm. (c) Chemical shift of the hg protons of MTAB-AuNS as a function of particle diameter. (d) T2 (orange) and T2* (blue) relaxation times of MTAB hg protons as a function of particle diameter. Reproduced from Wu, M.; Vartanian, A. M.; Chong, G.; Pandiakumar, A. K.; Hamers, R. J.; Hernandez, R.; Murphy, C. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4316–4327 (ref 37). Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. (B) (a) 1H NMR spectra of CdTe-TGA QDs (blue) and free TGA (red). (b) 2D-DOSY spectra of CdTe-TGA QDs, showing the separation of TGA bound to QDs (orange) and the free TGA (gray). Reproduced from Bonilla, C. A. M.; Flórez, M.-H. T.; Molina Velasco, D. R.; Kouznetsov, V. V.New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 8452–8458 (ref 20). Copyright 2019 Royal Society of Chemistry. (C) (a) PAH-functionalized nanodiamond. (b) The expanded view of the 2D-TOCSY spectrum of PAH-DNP. The low amplitude cross peaks are circled (A and B). (c) Selective-1D TOCSY and standard 1H NMR of PAH-DNP. Reproduced from Zhang, Y.; Fry, C. G.; Pedersen, J. A.; Hamers, R. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12399–12407 (ref 42). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society.
