FIGURE 1.
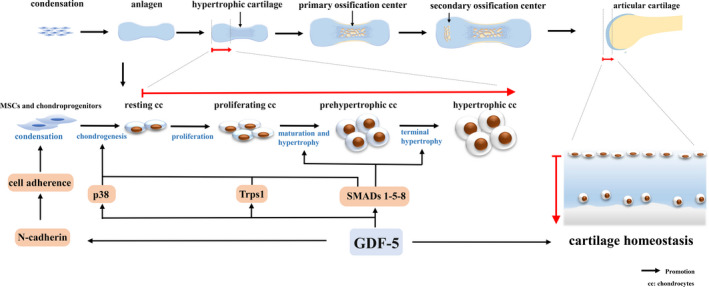
The role of GDF‐5 during cartilage development. The process starts with mesenchymal stem cell (MSCs) condensation. Condensed cells are differentiated into chondrocytes that construct a cartilage template (anlagen) by synthesizing ECM. Chondrocytes at the centre of condensation become hypertrophic and hypertrophic cartilage is calcified. These terminally differentiated chondrocytes undergo apoptosis and are replaced by the calcified bone in the primary ossification centre. Later, the secondary ossification centre is newly developed at the epiphysis and radially spreads within it. The part between the secondary ossification centre and the joint cavity is permanently retained as articular cartilage. During cartilage development, GDF‐5 promotes mesenchymal cell condensation and differentiation into chondrocytes and further stimulates chondrocytes differentiating into proliferative, prehypertrophic and hypertrophic cells. In articular cartilage, GDF‐5 functions to maintain cartilage homeostasis
