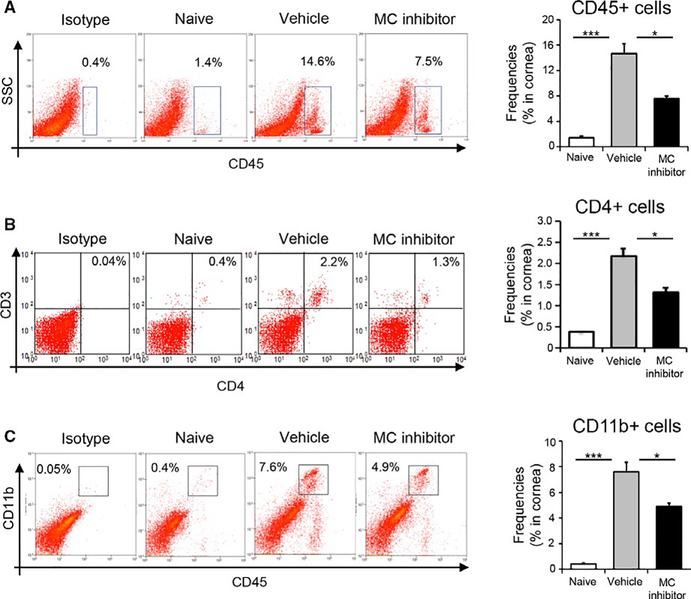
FIGURE 6.
Inhibition of mast cell function reduces the infiltration of alloimmune-inflammatory cells into the graft. (A) Representative flow cytometric dot plots (left) and cumulative bar chart (right) showing frequencies of CD45+ inflammatory cells in the corneas of naïve, vehicle-treated, and mast cell inhibitor-treated groups at 2 weeks posttransplantation. (B) Representative flow cytometric dot plots (left) and cumulative bar chart (right) showing frequencies of CD4+ T cells in the corneas of naïve, vehicle-treated, and mast cell inhibitor-treated allograft recipients at 2 weeks posttransplantation. (C) Representative flow cytometric dot plots (left) and cumulative bar chart (right) showing frequencies of CD11b+ myeloid immune cells in the corneas of naïve, vehicle-treated, and mast cell inhibitor-treated groups at 2 weeks posttransplantation. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown and each experiment consisted of five animals. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (error bar). t test, *P < .05, ***P < .001