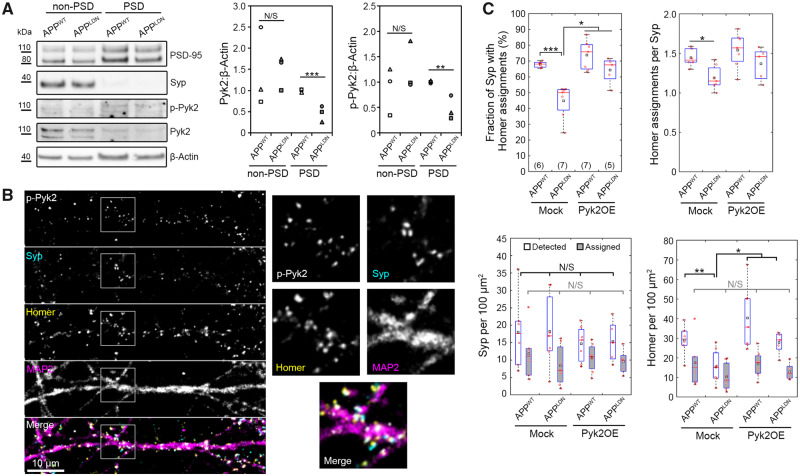
Figure 4.
Pyk2 overexpression in postsynaptic neurons blocks the synaptotoxicity due to CHO-APPLDN co-culture. (A) Exemplary immunoblots and quantification of the PSD fraction following synaptosome extraction at DIV14 following 16-h-long treatment with the indicated CHO cell medium. N = 3 independent experiments. Unpaired t-test. (B) An exemplary immunofluorescence image of the synaptic chamber at DIV14 showing p-Pyk2, Syp, Homer 1 and MAP2. Boxed areas are 2.5× magnified. (C) Synaptic read-outs following Pyk2 overexpression in postsynaptic neurons from DIV7 to DIV14. Each Homer spot was assigned to the nearest Syp spot within a cut-off distance of 1.0 μm (see Supplementary Fig. 1 for details). Following the assignment of all Homer spots, the fraction of Syp spots assigned by at least one Homer spot and the average number of Homer assignments per Syp spot were calculated. Densities of all Syp and Homer spots detected (white), Syp spots assigned by a Homer spot (grey) and Homer spots assigned to a Syp spot (grey) are also shown. In box plots, red circles, red bars and black squares indicate individual data points, sample median and sample mean, respectively. Numbers of microfluidic devices analysed (obtained from at least three independent cultures) are given in parentheses. Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA, followed by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Error bars = SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005. N/S = not significant.