Figure 1. ASF1A phosphorylation at Ser-166 is required for its interaction with MDC1 on DSBs.
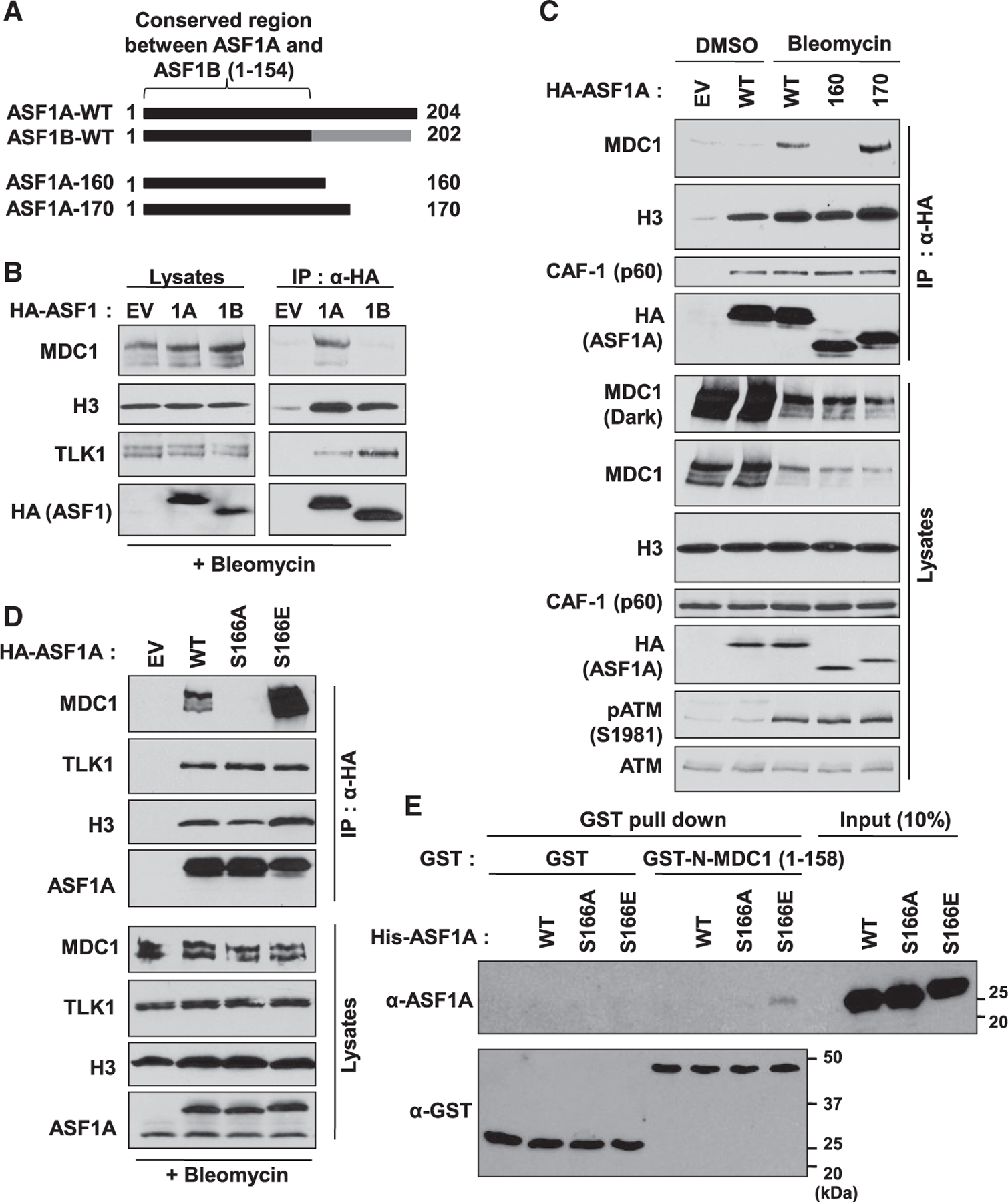
(A) Poor conservation of C-terminal ASF1A and ASF1B in humans, and C-terminal deletion mutants of ASF1A with HA tag used in (C).
(B) MDC1 interaction with ASF1A, not ASF1B, in presence of DSBs. HA-tagged ASF1A or ASF1B was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody conjugated beads in HEK293T cells after 20 µg/mL bleomycin treatment for 1 h. Shown are immunoblots of immunoprecipitates and lysates. EV, empty vector; 1A, HA-ASF1A; 1B, HA-ASF1B.
(C) 160–170 amino acids of C-terminal ASF1A required for its interaction with MDC1. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed as described in (B).pATM, a marker for DSBs.
(D) Phospho-mimetic mutation of Ser-166 in ASF1A facilitates its interaction to MDC1. The wild-type (WT), Ser166Ala (S166A) or Ser166Glu (S166E) mutant of HA-ASF1A was applied to the IP.
(E) In vitro binding of the phospho-mimetic ASF1A to recombinant FHA domain of MDC1. Recombinant GST or GST-tagged FHA domain of MDC1 (aa 1–158) was incubated with recombinant WT or S166 mutants of his-tagged ASF1A and then immunoprecipitated by glutathione beads followed by immunoblotting against the indicated antibodies.
