Figure 4. Chk1 phosphorylates Ser-166 of ASF1A on DSBs.
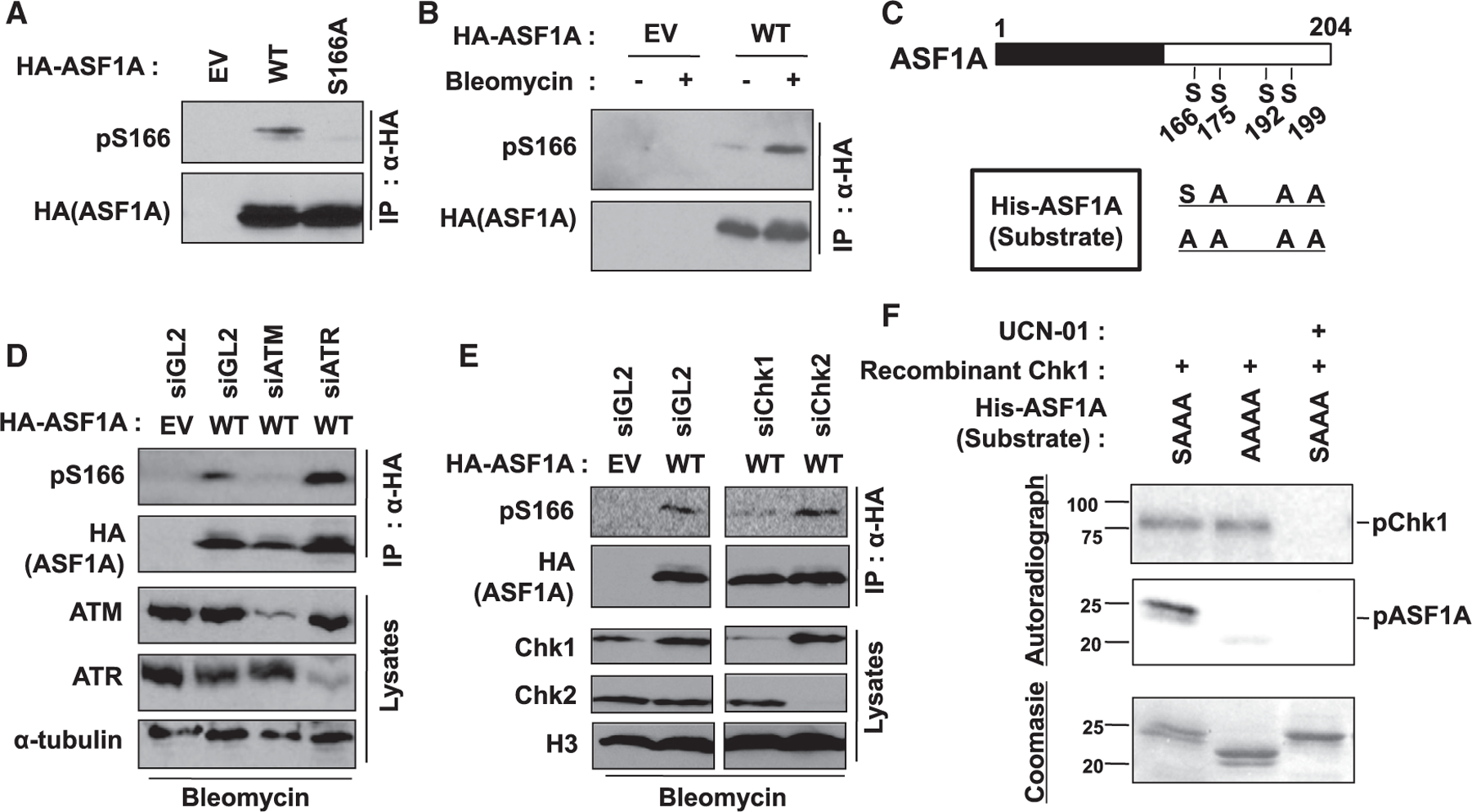
(A) Specific recognition of phosphorylated S166 in ASF1A using anti-pS166 antibody. HA-ASF1A WT or S166A mutant in HEK293T was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted by indicated antibodies. pS166, anti-phospho-S166 antibody.
(B) Increase of phospho-S166 in ASF1A on DSBs. HEK293T cells transfected by EV or HA-ASF1A WT plasmids were incubated with or without 10 µg/mL bleomycin for 14 h.
(C) A schematic of recombinant ASF1A used as substrates in vitro kinase assays.
(D and E) ATM and Chk1 required for pS166. Indicated siRNAs were transfected twice with 24 h-interval in HEK293T cells having transient expression of HA-ASF1A WT.
(F) Chk1 directly phosphorylates S166 of ASF1A in vitro. In vitro Chk1 kinase assay was performed as described in the STAR methods. Chk1 kinase activity and S166 phosphorylation in the reactions were chased by radio-labeling of recombinant Chk1 and ASF1A, respectively. 1 µM UCN-01 was treated to inhibit Chk1 activity.
