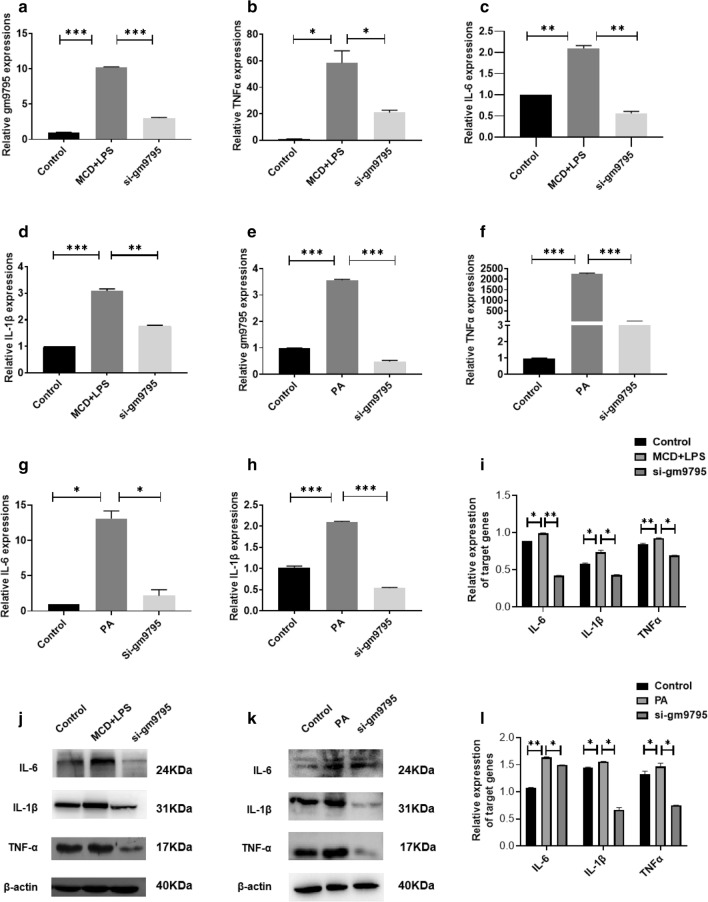
Fig. 4.
Knocking down LncRNA-gm9795 significantly decreased the expression of inflammation factors in NASH: a Interference efficiency of siRNA-gm9795 in MCD+LPS model; b In MCD+LPS model, the mRNA expression of TNF was decreased after knocking down gm9795; c In MCD+LPS model, the mRNA expression of IL-6 was decreased after knocking down gm9795; d In MCD+LPS model, the mRNA expression of IL-1 was decreased after knocking down gm9795; e Interference efficiency of siRNA-gm9795 in PA model; f. In PA model, the mRNA expression of TNF was decreased after knocking down gm9795;g. In PA model, the mRNA expression of IL-6 was decreased after knocking down gm9795; h In PA model, the mRNA expression of IL-1 was decreased after knocking down gm9795; i Relative gray analysis of protein expression of inflammation factors with gm9795 interference in MCD+LPS model; j The protein expression of inflammation factors was decreased after knocking down gm9795 in MCD+LPS model; k The protein expression of inflammation factors was decreased after knocking down gm9795 in PA model; l Relative gray analysis of protein expression of inflammation factors with gm9795 interference in PA model; (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01,***P < 0.001)