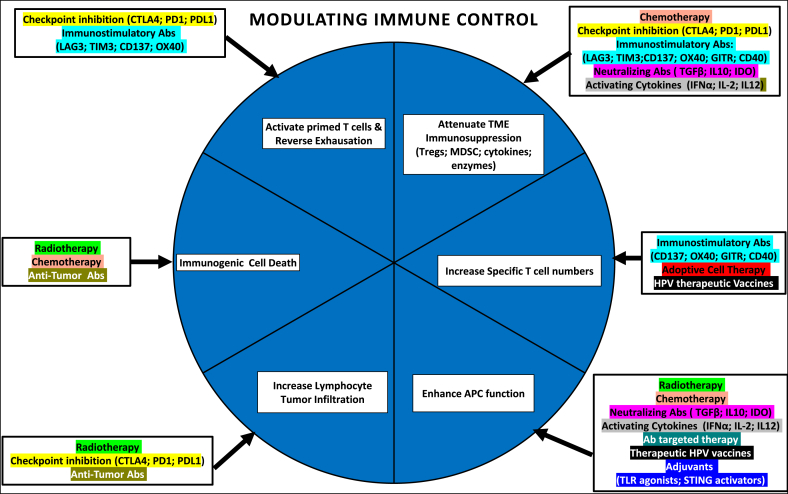
Fig. 2.
Potential synergies in combined immunotherapies [after 107]
Citations for examples of antibodies: for immune-stimulation [108]; direct anti-tumour therapy [109] neutralising cytokines [110,111]; activating cytokines [112]. Effector and targets: Abs, antibodies; LAG3 negatively regulates cellular proliferation, activation/homeostasis of T cells; CD137 crosslinking enhances T cell proliferation, IL-2 secretion, survival and cytolytic activity; OX40, a tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily member acts as a secondary co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule, expressed after 24 h after activation; GITR, (glucocorticoid-induced tumour necrosis factor receptor) is a surface receptor molecule involved in inhibiting the suppressive activity of T-regulatory cells and extending T-effector cell survival; CD40 is a costimulatory protein found on APC and required for their activation so agonistic Abs activate an anti-tumour T cell response via activation of dendritic cells; TGFβ, transforming growth factor beta is a pleiotropic cytokine that can exhibit both tumour-suppressive and oncogenic functions; IDO, indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 is a rate-limiting enzyme that metabolizes the essential amino acid, tryptophan, to kynurenine which leads to inhibition of immune cell effector functions and/or facilitates T cell death.