Fig. 3. Epitope mapping of PvRBP2b human mAbs.
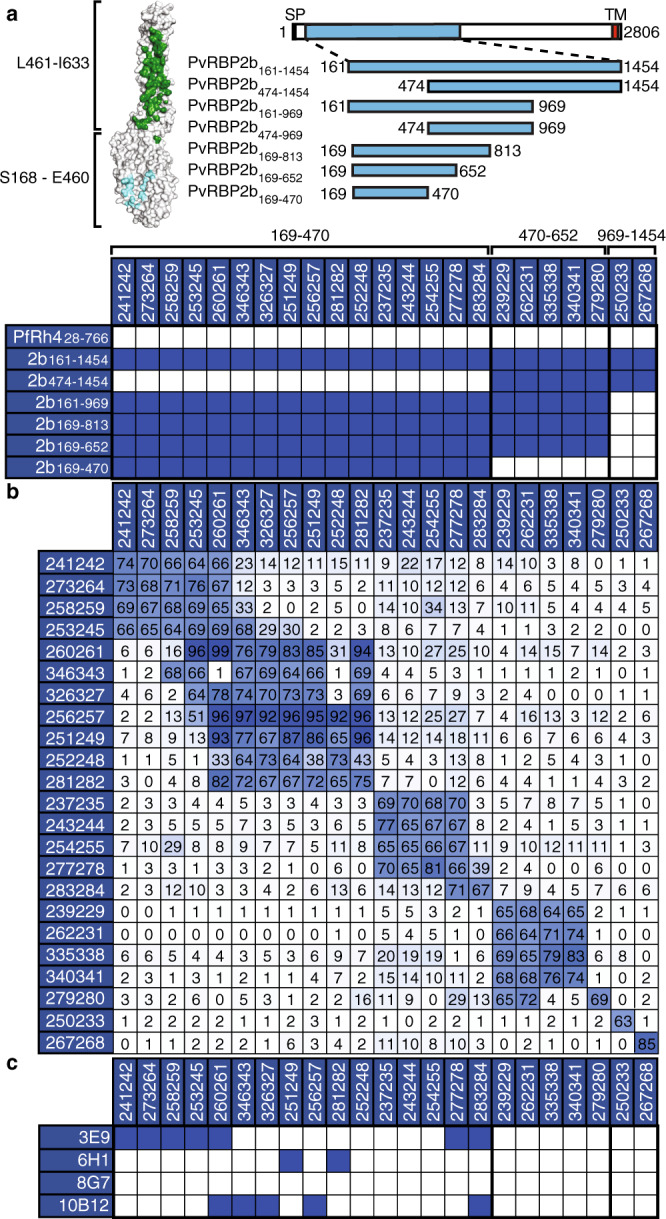
a (Left) Surface representation of PvRBP2b from the cryo-EM ternary complex structure (PDB accession code 6D04). PvRBP2b residues S168–E460 and L461-I633 are demarcated to show the domains that mainly interact with Tf (cyan) and TfR1 (green), respectively. (Right) Schematic representation of full-length PvRBP2b and recombinant protein fragments. Numbers indicate N- and C-terminal amino acid residues. SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain (red box). (Bottom) Mapping of PvRBP2b human mAbs using recombinant protein fragments. Blue boxes represent signals that are >10-fold higher compared to PfRh4. The amino acid region to which human mAbs bind are indicated above the table. b Competition ELISA using immobilized PvRBP2b human mAbs indicated on the left column incubated with a mixture of human mAbs indicated on the top row and PvRBP2b161–1454 using a 20:1 molar ratio. Inhibition of PvRBP2b161–1454 binding in the presence of antibody in solution was calculated relative to PvRBP2b161–1454 binding in the absence of antibody in solution. A blue to white gradient shows antibodies with the highest levels of competition in dark blue and the lowest in white. Competition (>60% inhibition of PvRBP2b161–1454 binding), partial competition (between 30 and 59%), no competition (<29%). c Competition ELISA using immobilized PvRBP2b-mouse mAbs incubated with a mixture of human mAbs and PvRBP2b161–1454 at a 20:1 molar ratio. Blue boxes indicate competition.
