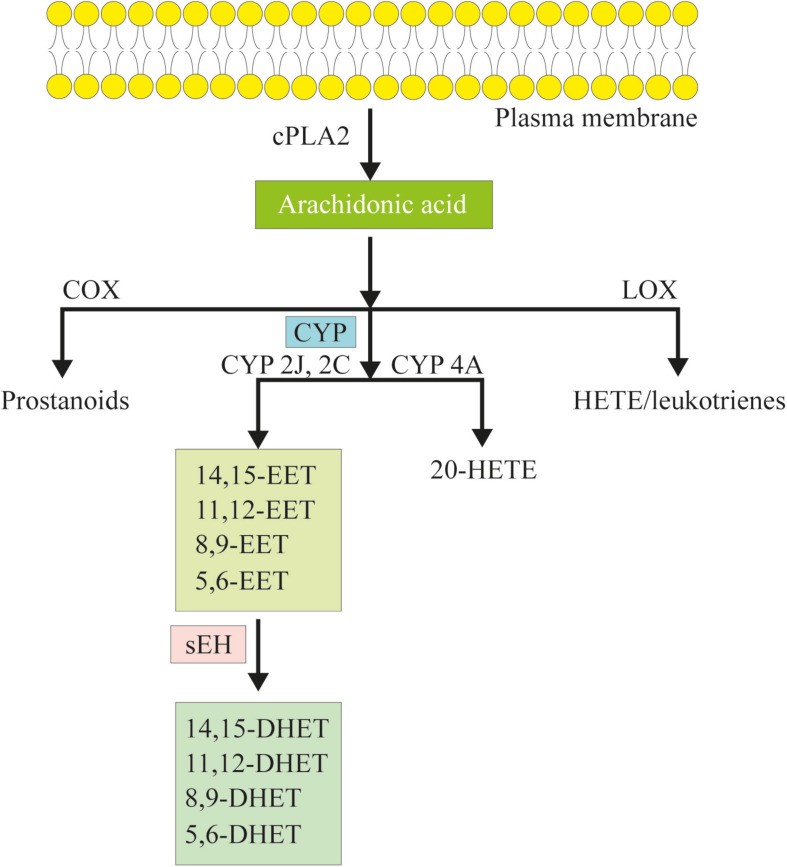
FIGURE 1.
The cascade of arachidonic acid (AA). AA is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid which is released from the membrane phospholipids in the presence of phospholipase a2 (cPLA2). AA can be metabolized to eicosanoids through three major pathways: the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway, the lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway, and the cytochrome P450 (CYP) pathway. In the CYP pathway, AA is converted to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and 20-hydroxy eicosatetraenoic acid (HETE) by CYP epoxygenases and CYP ω-hydroxylases. Following, EETs can be hydrated in vivo to dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs) by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH).