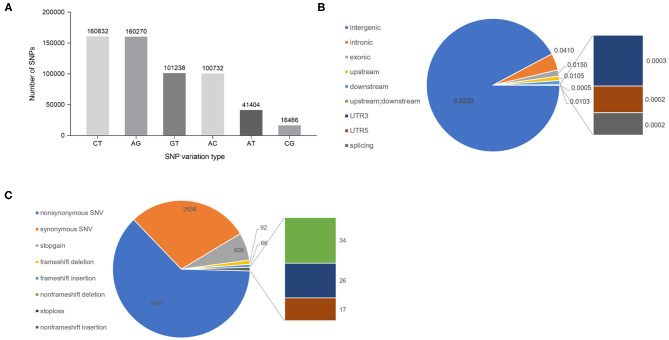
Figure 1.
Analysis of SNPs in cigar tobacco genomes. (A) The six SNP types and the number of SNPs of each type. (B) The positions of the SNPs in the gene structures. Upstream: the SNP is located in the region 1 kb upstream (5′) of a gene; Downstream: the SNP is located in the 1-kb region downstream (3′) of a gene; splicing: variable splicing site within 2 bp. (C) Annotations of the SNPs in the exons. Non-synonymous SNV: a single-nucleotide change that causes an amino acid change; Synonymous SNV: a single-nucleotide change that does not cause an amino acid change; Stop gain: the mutation causes early termination of translation; Stop loss: the variation causes the loss of the terminator codon.