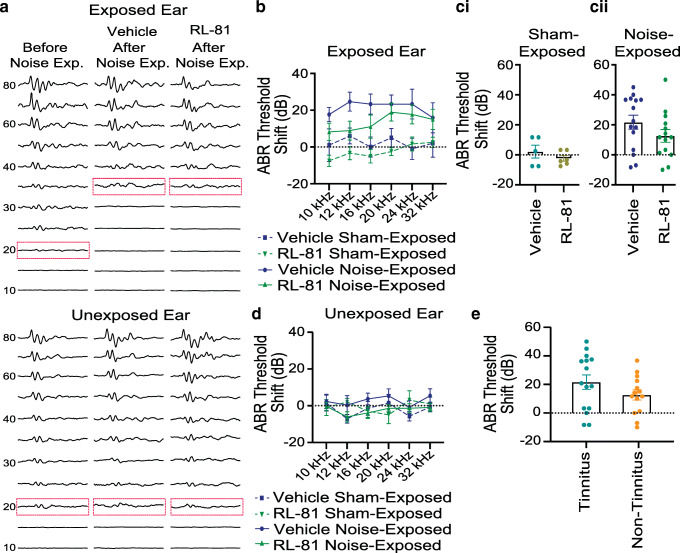
Fig. 3.
Transient RL-81 IP application 1 week after noise exposure had no effect on noise-induced hearing loss, assessed 3 weeks post noise exposure. a Representative traces of ABR recordings (in response to 12 kHz tones) with thresholds highlighted (dotted rectangle) before and 3 weeks post noise exposure in vehicle- and RL-81-treated mice for exposed (top) and unexposed (bottom) ear. b ABR threshold shifts in the exposed ear in vehicle vs. RL-81 in noise- and sham-exposed mice (NE: N = 15 vehicle; 14 RL-81; SE: N = 5 vehicle; 6 RL-81; 3-way ANOVA exposure: F (1,203) = 41.25, P < 0.0001; drug condition: F (1,203) = 5.375, P = 0.021). c Effect of RL-81 on ABR threshold shifts from sham- (ci) and noise-exposed (cii) mice (sham-exposed: N = 5 vehicle, 6 RL-81; unpaired t test: t (9) = 1.029, P = 0.33; noise-exposed: N = 15 vehicle, 14 RL-81; unpaired t test: t (27) = 1.448, P = 0.16). d ABR threshold shifts in the unexposed ear in vehicle vs. RL-81 in noise- and sham-exposed mice (NE: N = 15 vehicle; 14 RL-81; SE: N = 7 vehicle; 5 RL-81; 3-way ANOVA exposure: F (1,210) = 0.75, P = 0.39; drug condition: F (1,210) = 1.123, P = 0.29). e Average ABR threshold shifts across frequencies in tinnitus assessed mice (N = 14 non-tinnitus, 15 tinnitus: t (27) = 1.416, P = 0.17)