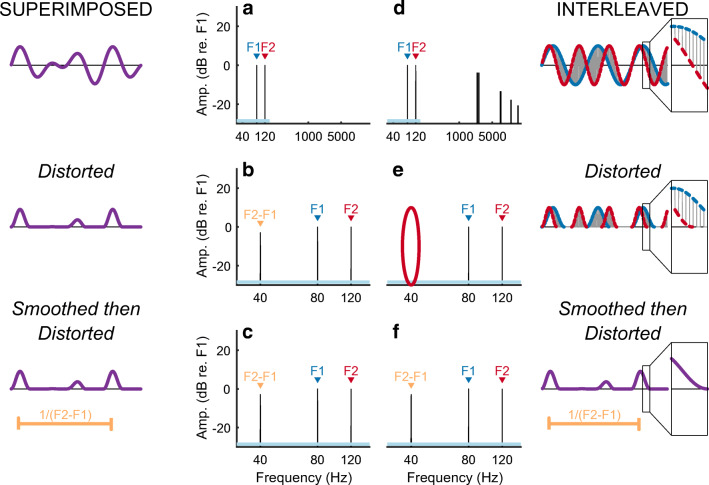
Fig. 1.
A) Frequency spectrum of an analogue dyad consisting of two superimposed sinusoids F1 (80 Hz) and F2 (120 Hz). A 35-ms portion of the waveform is shown on the left. B) An instantaneous nonlinearity (such as could occur in the stimulating device), consisting of half-wave rectification and squaring, results in a DP with frequency F2-F1 = 40 Hz. This DP is also observed when the nonlinearity is preceded by smoothing, such as may occur in the auditory system (C). D) Stimulus produced by interleaving 200-μs sections of 80- and 120-Hz sinusoids. A zoomed-in section of the waveform is shown in the box on the far right. The nonlinearity now fails to produce a DP (part E, red oval) unless preceded by smoothing (F)