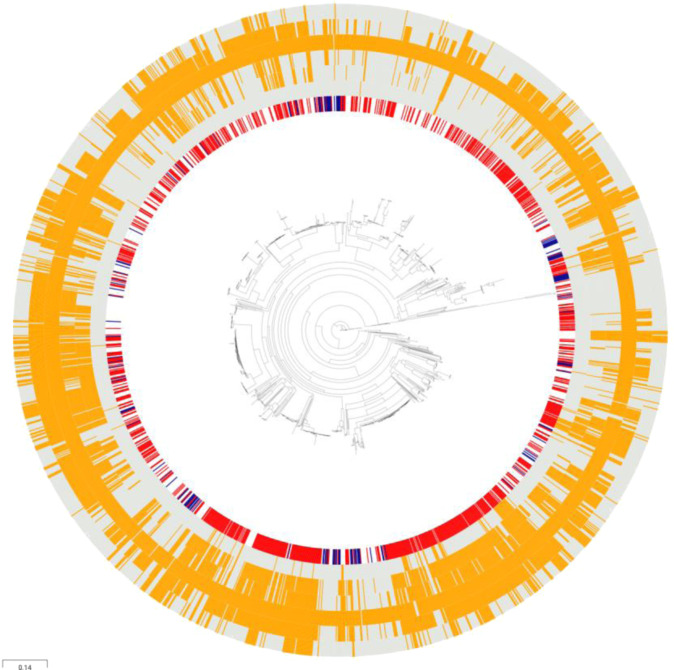
Fig. 6. Collection-wide antimicrobial resistance gene (ARG) patterns of E. faecalis depict abundance of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), also in isolates representing widely different host types.
Presence of acquired and apparent intrinsic ARGs is aligned with the species-wide (n = 2027) reference mapping-based maximum likelihood phylogeny. Inner ring, selected isolation source: hospitalised patient (red) and wild bird (dark blue). Outer rings, presence (orange) and absence (grey) of selected major ARG classes as defined by using Antimicrobial Resistance Identification By Assembly (ARIBA) v.2.14.488 against ResFinder 3.2 database81, from inner to outermost ring: vancomycin (glycopeptide), aminoglycosides, macrolides, lincosamides, tetracyclines and phenicols. In addition, five isolates were identified carrying acquired ARGs to linezolid, of which one was cfrD, two were optrA and two poxtA. The illustration was created using Microreact77. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.