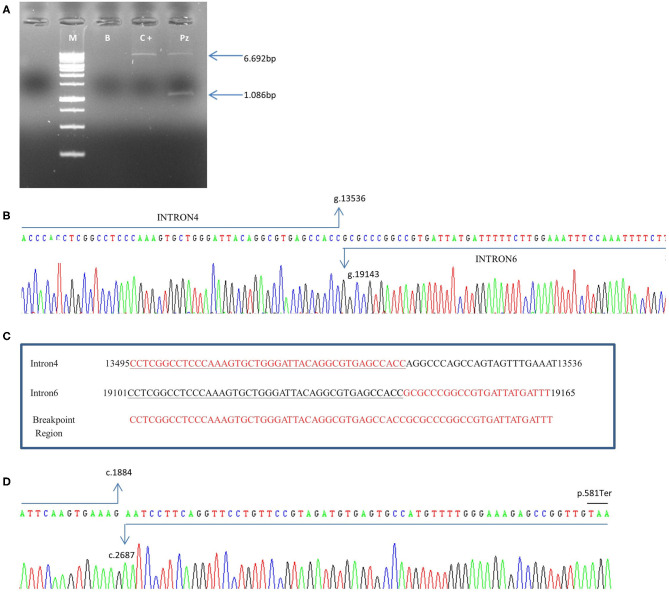
Figure 4.
Characterization of exon 5–6 deletion in the PALB2 gene. (A) Genomic DNA was amplified using specific deletion primers (Del4F and Del7R). The mutant allele gives rise to a specific 1.086-bp fragment. M: marker, B: blank, C+: wild-type control, Pz: patient. (B) The electropherogram of the 1.086 bp PCR fragment, containing the deletion breakpoint, showed a wild-type sequence until the nucleotide g.13536C (NG_007406.1) of PALB2 intron 4. The following sequence corresponded to the PALB2 intron 6 starting from the g.19143G nucleotide (NG_007406.1). (C) An homologous sequence of 43 nucleotides (underlined nucleotides), identified at breakpoint region, represents the cause of the rearrangement. (D) Electropherogram showing the sequence of the PCR product of 152 bp obtained from cDNA patient. Sequencing analysis revealed a wild-type sequence until the nucleotide c.1884G (NM_024675.3) of PALB2 gene in exon 4. The following sequence corresponded to the PALB2 exon 7 starting from the nucleotide c.2687A (NM_024675.3). A premature stop codon produces a truncated protein of 581 amino acids.