FIG 4.
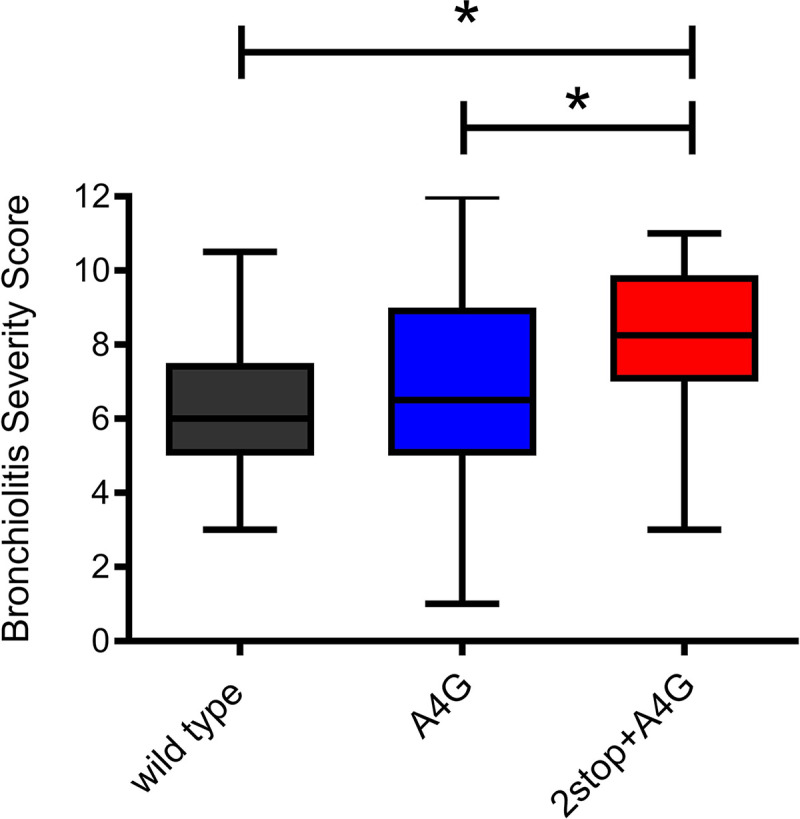
Bronchiolitis severity scores (BSS) associated with RSV genotypes in the TCRI cohort. The BSS (BSS scale 0 to 12, with higher numbers indicating more severe disease) of the 209 infants with RSV infection whose virus was sequenced were compared to identify differences in BSS by RSV genotype (wild type, n = 23; A4G, n = 82, and 2stop+A4G, n = 37). The 2stop+A4G genotype, containing two tandem stop codons in the C-terminal region of the G gene, was associated with clinically significant differences in disease severity in comparison to that for single stop codon (A4G) and wild-type A2-like viruses. Box plots represent median BSS (middle line), interquartile range (length of the box, 25th and 75th), and maximum/minimum values (the whiskers show the extent of the data range). Statistical comparisons indicated on the figure were performed using the Wilcoxon or Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric tests. In multivariable ordinal logistic regression analysis, the 2stop+A4G genotype was associated with significantly increased likelihood of higher bronchiolitis scores than both the wild type (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 3.00; 95% CI, 1.23 to 7.28) and A4G genotypes with 2stop (aOR = 2.42; 95% CI, 1.21,4.86). *, P < 0.05.
