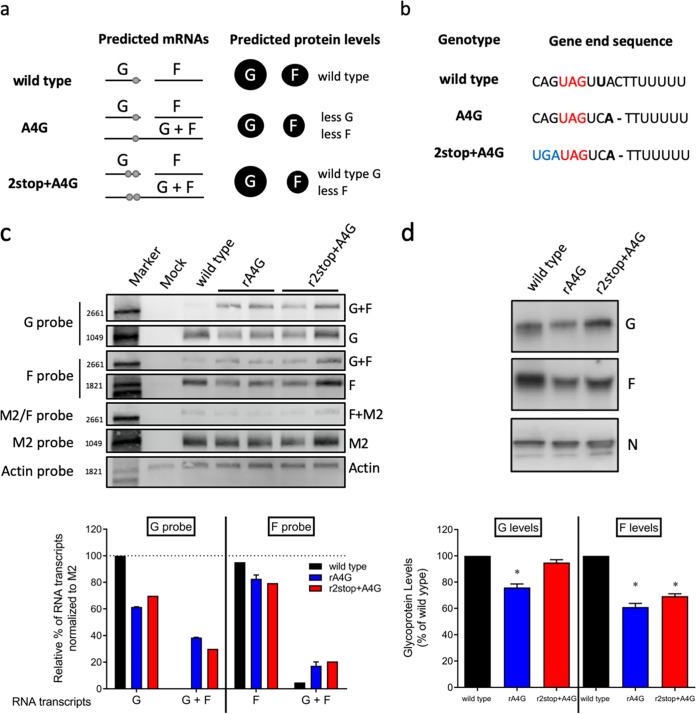
FIG 5.
Effects of A4G and 2stop+A4G genotypes on RSV glycoprotein transcription and expression levels. (a) Hypothesized mRNA transcription and protein expression by wild-type A2-like, A4G, and 2stop+A4G genotypes. Each horizontal line indicates a predicted mRNA transcript. Light gray dots indicate stop codons present on single G transcripts or on G/F cotranscripts. The size of the black circles under “predicted protein levels” indicate the expected relative levels of each glycoprotein. (b) Comparison of RSV wild type, A4G and 2stop+A4G genotype G gene end sequences. (c) Representative Northern blots performed using probes specific for RSV G, F, M2, or mammalian actin mRNA as a control. Two virus clones of recombinant rA4G and r2stop+A4G RSV were tested. G, F, and G/F cotranscripts were quantified as a percentage of total transcripts detected with G- or F-specific probes. rA2-K-Line19F was used as the wild-type A2-like control. Data from both clones of rA4G and r2stop+A4G viruses were combined and presented as means plus standard deviation (SD). (d) Representative RSV N-, G-, and F-specific Western blots of rA4G, r2stop+A4G, and wild-type (rA2-K-Line19F) viruses. Quantification of three replicates of Western blots were calculated for rA4G, r2stop+A4G, and wild type rA2-K-Line19F viruses by densitometry. G and F levels were normalized to N levels for each virus prior to comparison with wild-type rA2-K-Line19F. Data represent means from 3 experimental replicates plus SD. *, P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test.