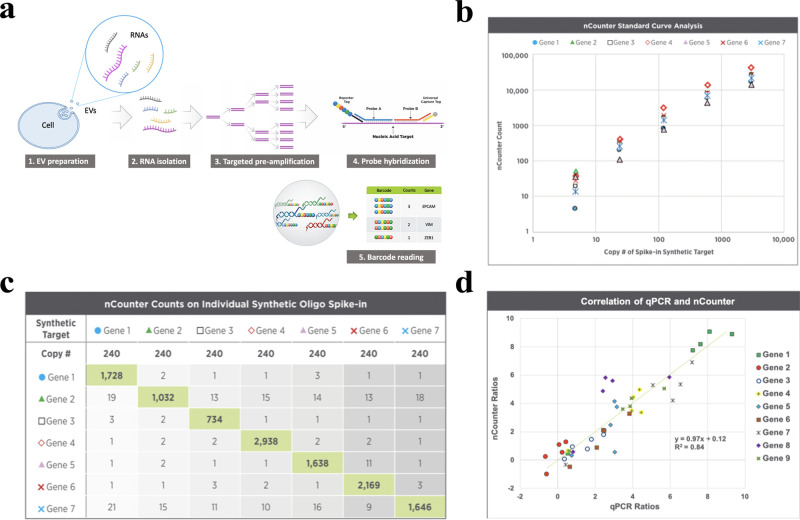
Figure 1.
Introduction and validation of the NanoString low RNA input nCounter assay. (a) A schematic diagram of the workflow of the nCounter Low RNA Input Kit. The EV RNAs are first converted to cDNA. The targets of interest are further selectively amplified using the multiplex low-input primer pool with 14 cycles of PCR. The amplified products are then hybridized with the nCounter panel following the standard nCounter hybridization protocol. (b) Amplification efficiency was analyzed using 7 spike-in synthetic DNA oligo targets selected from the nCounter RNA panel. The mean primer efficiency is 86% by the standard curve analysis on a 1:5 serial dilution of the synthetic oligo targets from 5 to 3000 copies of spike-in molecules. (c) Amplification specificity was analyzed by spiking in 240 copies of each synthetic oligo target into a background of universal human reference RNA (UHRR) cDNA. No off-target false amplification is observed. (d) Correlation of real-time qPCR and nCounter assay assessed by analyzing nine preselected genes in five cell-free RNA samples. nCounter ratios: Ratios of normalized counts of cfRNA samples to the reference RNA (UHRR). qPCR ratios: Ratios of cycle threshold values cfRNA samples to UHRR. Ratios correlate well between nCounter and qPCR (R2 = 0.84).