Figure 3.
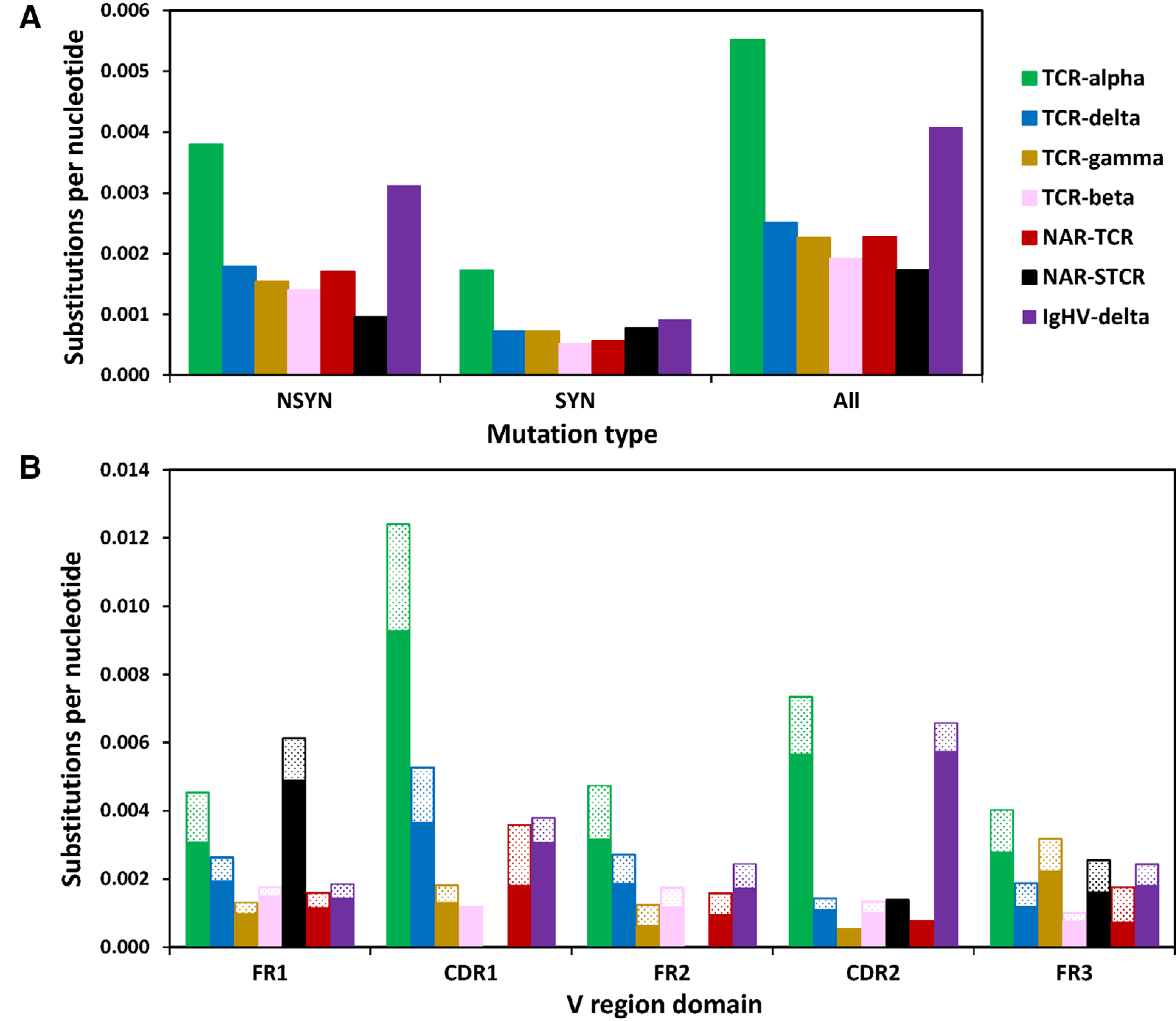
SHM targets complementarity-determining regions (CDR) of TCR-α associated with alpha constant regions. (A) TCR-α accumulates significantly more nonsynonymous (NSYN, solid) mutations than all other TCR chains except IgHV-δ sequences and significantly more synonymous (SYN, stippled) mutations than all other chains. (B) TCR-α/δ V gene segments associated with TCR-α constant (C) regions accumulate significantly more mutations in both framework (FR) and CDR than when associated with TCR-δ C, and in general, accumulate significantly more mutation than all other TCR chains except CDR2 domains of IgHV-δ (Student’s one-way, unpaired t-test, p < 0.01). We counted the number of mutations within 422 TCR-α/δ V-TCR-α C (green), 137 TCR-α/δ V-TCR-δ C (blue), 158 TCR-γ V (gold), 237 TCR-beta V (pink), 51 NARTCR V (red), 62 supporting NARTCR-δ V (NAR-STCR, black), and 275 IgHV-TCR-δ C (purple) sequences (Student’s one-way, unpaired t-test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). Data from a single experiment, where each PCR tube represents a single replicate for each chain, shark, and tissue sample (see Supporting information Tables 1 and 2).
