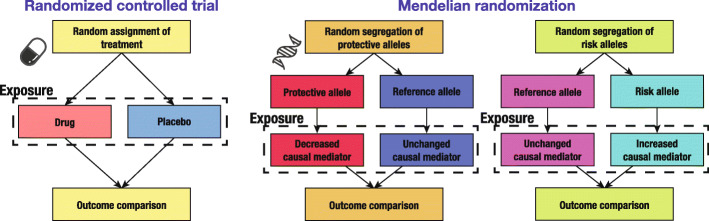
Fig. 1.
Schematic comparison between the randomized controlled trial and Mendelian randomization. Two schematic diagrams are shown for Mendelian randomization separately for the effect direction of the non-reference allele, i.e. protective or causal (risk allele). For simplicity, a single genomic locus is depicted in the diagrams of Mendelian randomization. Note that multiple loci are considered for statistical evaluation in practical settings. In RCT, random assignment of a treatment minimizes the effects of confounders. In MR, random segregation of alleles during gamete formation plays a similar role