Figure 7.
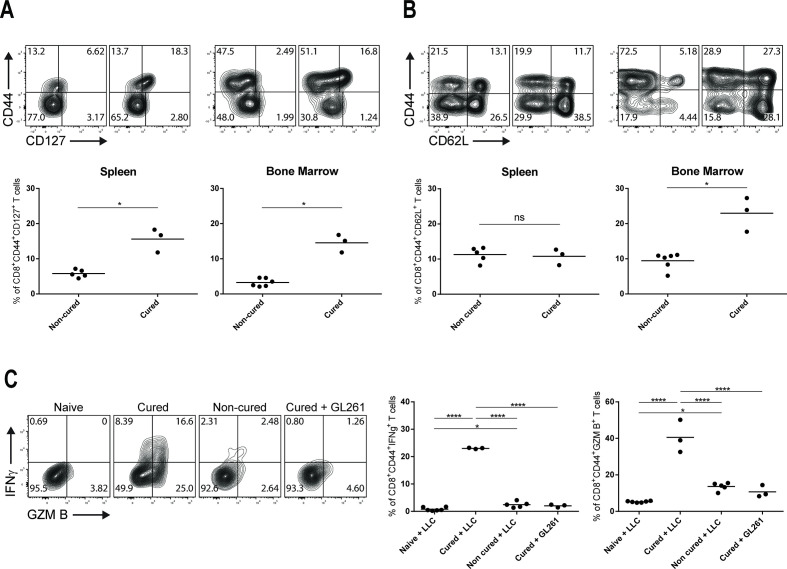
Anti-PD-L1-based trimodal therapy causes an accumulation of memory T cell subsets in lymphoid organs of cured LLC tumor-bearing mice. Representative flow cytometry dot plots and quantification of CD8+ CD44+ CD127+ memory T cells (A) and CD44+ CD62L+ central memory CD8+ T cells (B) from spleen and bone marrow of LLC tumor-bearing mice treated with 10 Gy+L19–IL2+anti-PD-L1 harvested 43±2.1 days after tumor cure (12 days after tumor rechallenge) or endpoint (T4×SV) had been reached. Cells were obtained from one experiment performed in figure 1B. Stainings, flow cytometry data acquisition, and analysis of the samples were done in independent duplicates. (C) Representative flow cytometry dot plots and quantifications of CD8+ CD44+ T cells expressing IFNγ and granzyme B from splenocytes of cured or non-cured LLC tumor-bearing mice treated with 10 Gy+L19–IL2+anti-PD-L1, or from naïve mice after co-culture with irradiated LLC target cells or GL261 as non-specific target cells. Cells were obtained from the same experiment as in (A) and (B). Co-culture assay, stainings, flow cytometry data acquisition, and analysis of the samples were done in independent duplicates. LLC, Lewis lung carcinoma.