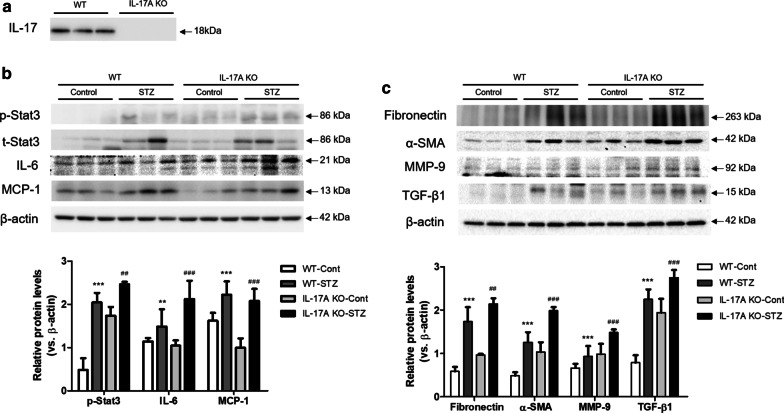
Fig. 2.
IL-17A deficiency exacerbates the expression of inflammatory cytokines and fibrosis-related proteins in STZ-induced DN. WT and IL-17A KO mice (n = 6/group) were injected with STZ (50 mg/mL) for 5 consecutive days (citrate buffer was administered to the control mice). The animals were euthanized 12 weeks after STZ injection. a Knockout of IL-17 was confirmed by Western blot analysis. b The expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, p-STAT3, and MCP-1) and fibrosis-related proteins (Fibronectin, TGF-β1, α-SMA, and MMP-9) in kidney homogenates was determined by western blotting analysis. c The band intensities were determined by densitometry using the ratios of IL-6, p-STAT3, MCP-1, Fibronectin, TGF-β1, α-SMA, and MMP-9 to β-actin. The mice were randomly assigned to four groups of six mice: (i) wild-type mice without STZ treatment (WT Cont group), (ii) STZ-treated WT diabetic mice (WT STZ group), (iii) IL-17A knockout (KO) mice without STZ treatment (IL-17A KO Cont group), and (iv) STZ-treated IL-17A KO diabetic mice (IL-17A KO STZ group). The data are expressed as means ± SEM. ** < 0.01 and *** < 0.001 versus control group; ##< 0.01 and ### < 0.001 versus WT STZ group