Fig. 1. The subiculum comprises projection neurons targeting distinct downstream areas.
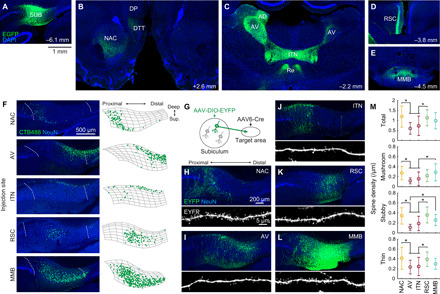
(A to E) After the injection of AAV1/2-EF1α-EGFP into the left dorsal SUB (A), EGFP-labeled axons were observed in the ipsilateral NAC, ipsilateral dorsal tenia tecta (DTT), ipsilateral dorsal peduncular cortex (DP) (B), bilateral AV, anterodorsal thalamic nucleus (AD), ITN, nucleus reuniens (Re) (C), the superficial layer of the ipsilateral granular RSC (D), and MMB (E). All images show coronal sections. Numbers, approximate distances of the sections from the bregma. (F) SUB coronal sections containing cholera toxin B subunit conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 (CTB488)–labeled projection neurons (left) and the corresponding cell counting (right). Left: Dotted curves, borders of the SUB cell layer. Right: Segmented SUB cell layer (mesh) and detected CTB488-positive neurons (dots). (G to M) Dendritic morphology of SUB projection neurons. (G) Schematic of visualization of projection-specific neuronal morphology. (H to L) SUB coronal sections containing EYFP-labeled projection neurons (top) and apical dendrites (bottom). The AAV6-pgk-Cre was injected in one of the following areas: NAC (H), AV (I), ITN (J), RSC (K), and MMB (L). (M) Dendritic spine density per unit length of the apical dendrite. n = 17, 17, 25, 21, and 20 cells for NAC-p, AV-p, ITN-p, RSC-p, and MMB-p SUB neurons, respectively. *P < 0.05, Tukey test. Means ± SD.
