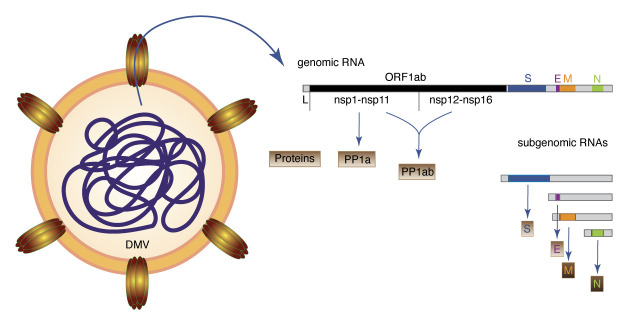
Figure 2. Replication and translation of viral genomic RNA.
Double-membrane vesicles (DMVs) contain double-stranded viral RNA, which is an intermediate of viral genomic RNA replication. Channels that span the double membrane allow viral RNAs, including positive-strand viral genomic RNA and subgenomic RNAs, to be exported. Translation of open reading frame 1a (ORF1a) gives rise to the polyprotein 1a (PP1a) comprising nsp1 to nsp11. A programmed ribosomal frameshift leads to transcription of PP1ab comprising nsp1 to nsp16. Subgenomic RNAs contain a common 5′ leader sequence and their translation gives rise to S (surface), E (envelope), M (membrane), and N (nucleocapsid) structural proteins. The 3′ part of the genome comprises additional ORFs (3a, 6, 7a, 7b, 8, and 10) that are not depicted. Their transcription leads to additional subgenomic RNAs (not shown). L, leader sequence.