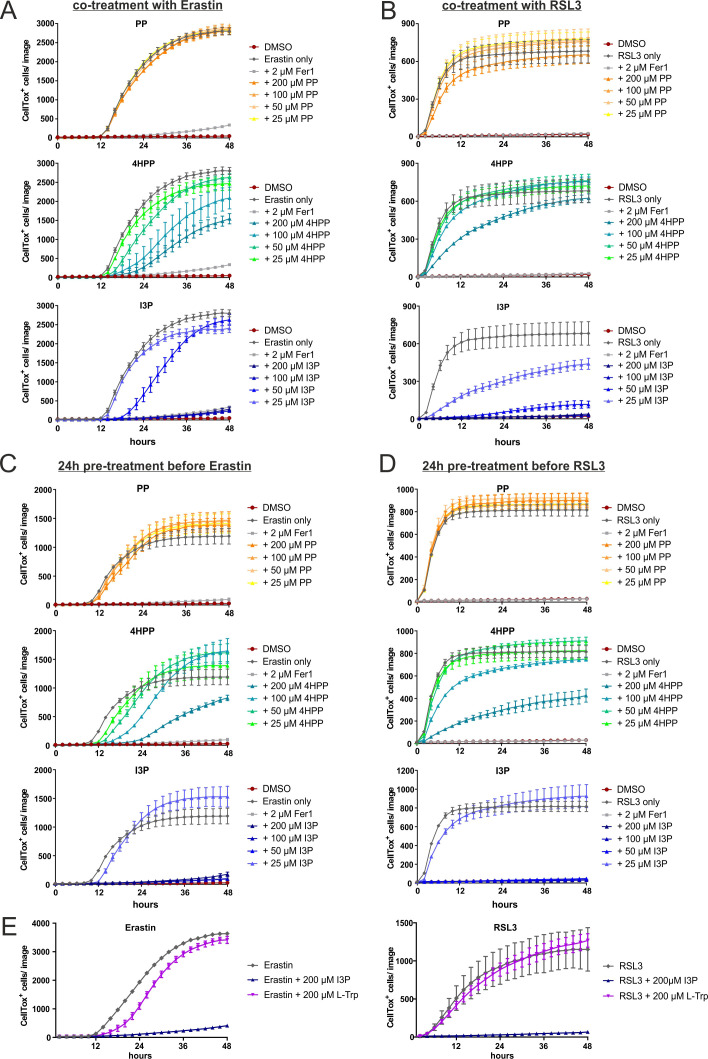
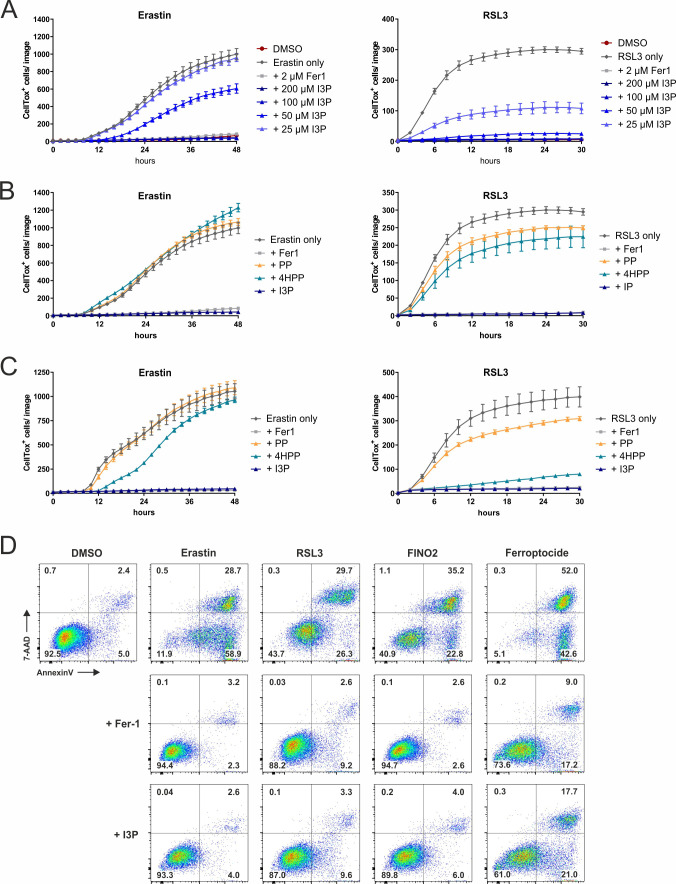
Figure 4. IL4i1 metabolites form an anti-ferroptotic hierarchy.
(A) Simplified schema of ferroptosis control showing the points of chemical perturbation by erastin and RSL3. (B) Quantification of cell death of HeLa cells treated with the ferroposis inducer erastin in the presence of 200 µM PP, 4HPP, or I3P by live cell imaging using CellTox straining. Ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) was added as a control to block erastin-induced death and has an equivalent suppressing effect as I3P. Right panel, representative CellTox staining images from an experiment similar to (B). (C) As in B, using RSL3 to induce ferroptosis. B,C: n = 3 biological replicates. The graphs are representative for three independent experiments. (D) I3P blocks lipid peroxidation induced by erastin and RSL3 determined by flow cytometry using C11-BODIPY. n = 3 biological replicates; data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test; ****p<0.0001. All error bars represent standard deviation. (E) Flow cytometry analysis of the anti-ferroptotic activity of I3P (200 µM) using Fer-1 as positive control. Murine NIH3T3 cells were treated with erastin, RSL3, FINO2, or ferroptocide to induce ferroptosis in the absence or presence of Fer-1or I3P and death quantified by 7-AAD and Annexin-V staining. See 'Materials and methods' for details of reagent concentrations and timing. The plots are representative for two independent experiments.