Figure 6. IL4i1 generates an anti-ferroptotic milieu.
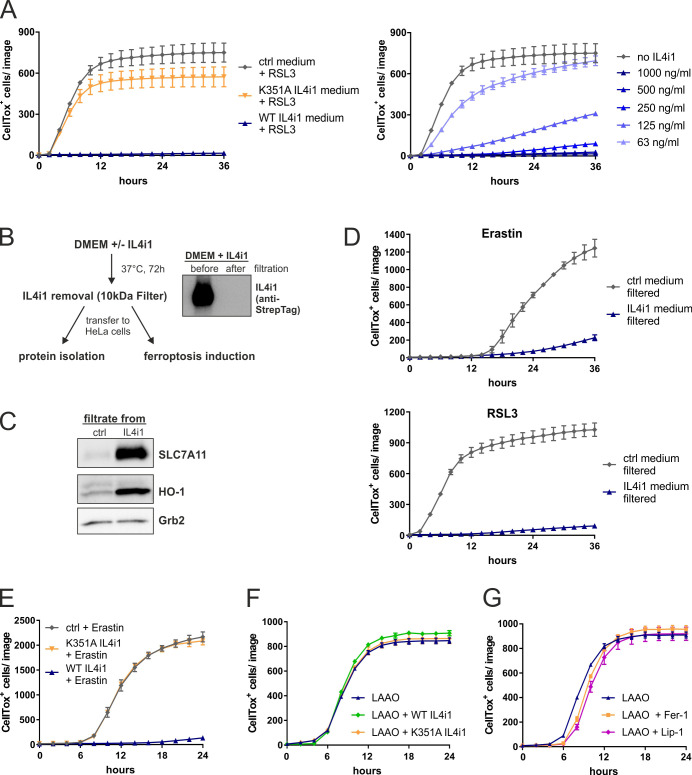
(A) Heat map of differentially expressed genes in HeLa cells after 24 hr incubation with IL4i1 (WT or K351A inactive mutant [Figure 2—figure supplement 1])-conditioned DMEM, 200 µM I3P, or untreated control medium. (B) Overlap of most significantly upregulated genes as compared to the untreated HeLa cells (adjusted p-value<10−9) in HeLa cells treated with I3P and WT IL4i1 conditioned medium. Many of the overlapping genes are associated with Nrf2 and AhR signaling. (C) I3P uptake by HeLa cells was quantified after 24 hr of incubation with IL4i1 conditioned DMEM by flow cytometry. n = 3 biological replicates; the graph is representative for three independent experiments. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparisons test; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; ns = not significant. (D, E) HO-1 or SLC7A11 expression was determined by immunoblotting following transfer of complete DMEM media treated with increasing concentrations of IL4i1 or enzyme-dead K351A mutant for 24 hr. (F) Quantification of erastin-induced ferroptosis in HeLa cells in the presence of IL4i1 conditioned DMEM. WT but not K351A mutant IL4i1 conditioned medium (1 µg/ml) suppressed ferroptosis (left). The anti-ferroptotic effect of IL4i1 is concentration dependent (right). n = 2 biological replicates; the graphs are representative for three independent experiments. All error bars represent standard deviation. (G) Schematic representation of the death-inducing versus death-protection mechanisms of venom LAAO versus mammalian IL4i1.