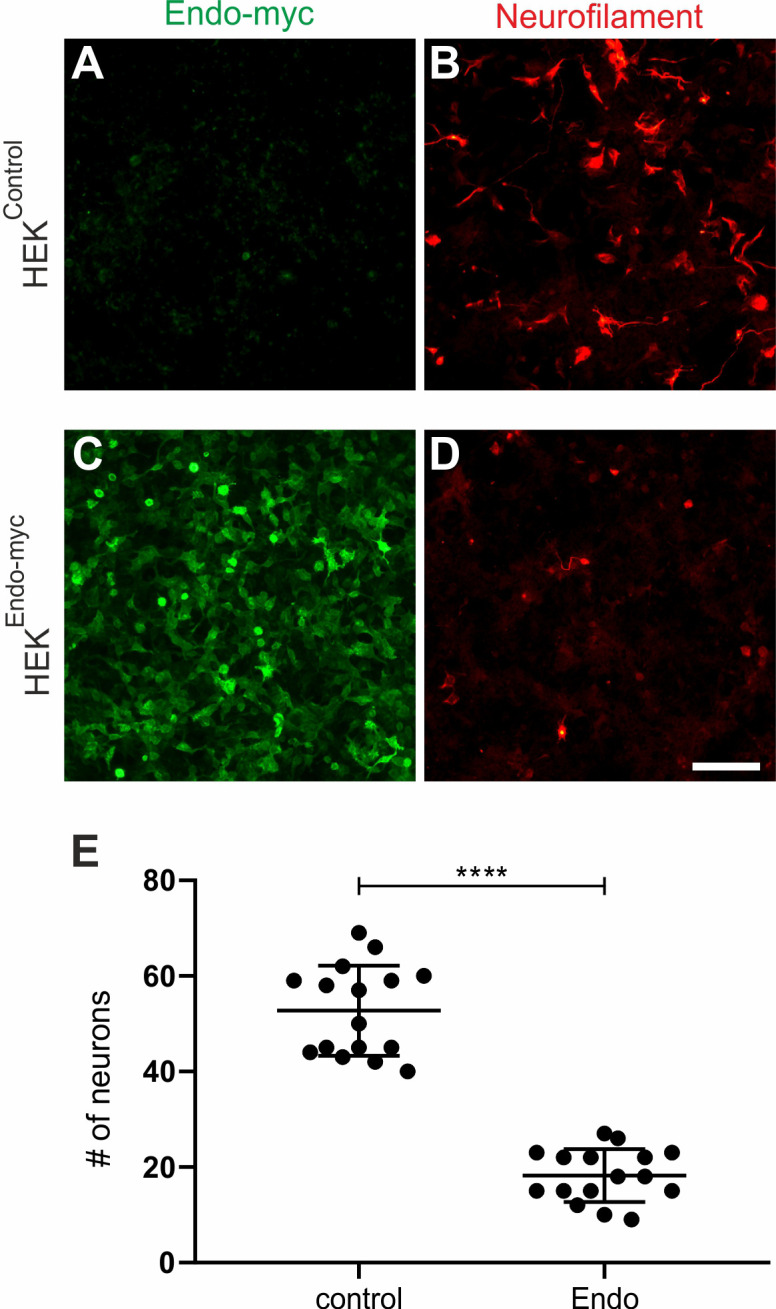
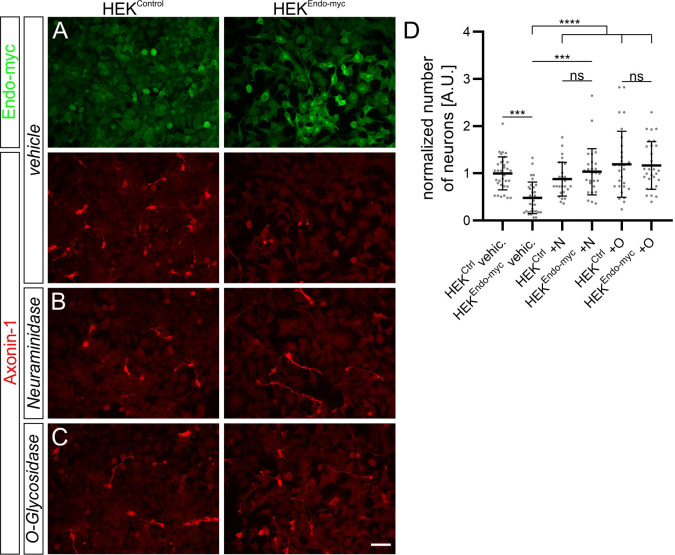
Figure 5. Endoglycan expression reduces adhesion of commissural neurons in vitro.
(A-C) Commissural neurons dissected from HH25/26 chicken embryos were cultured on a layer of control HEK cells or HEK cells stably expressing human Endoglycan. Neurons were allowed to attach for 16 hr. Staining for Axonin-1 revealed a pronounced decrease in the number of commissural neurons on HEK cells expressing Endoglycan compared to control HEK cells (A and D). For each replicate, the number of neurons attached to HEK cells expressing Endoglycan was normalized to the number of cells attached to control HEK cells (D). The number of commissural neurons attached to control HEK cells was more than twice the number on Endoglycan-expressing HEK cells (only 0.47 ± 0.34 compared to 1 ± 0.35). Treatment with Neuraminidase (+N) or O-glycosidase (+O) abolished the difference. See Table 2 for values. N(replicates)=4. ns (not significant), ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars represent standard deviations. O, O-glycosidase; N, Neuraminidase; vehic, vehicle; ctrl, control. Scale bar: 50 µm. Source data and statistics are available in Figure 5—source data 1 spreadsheet.
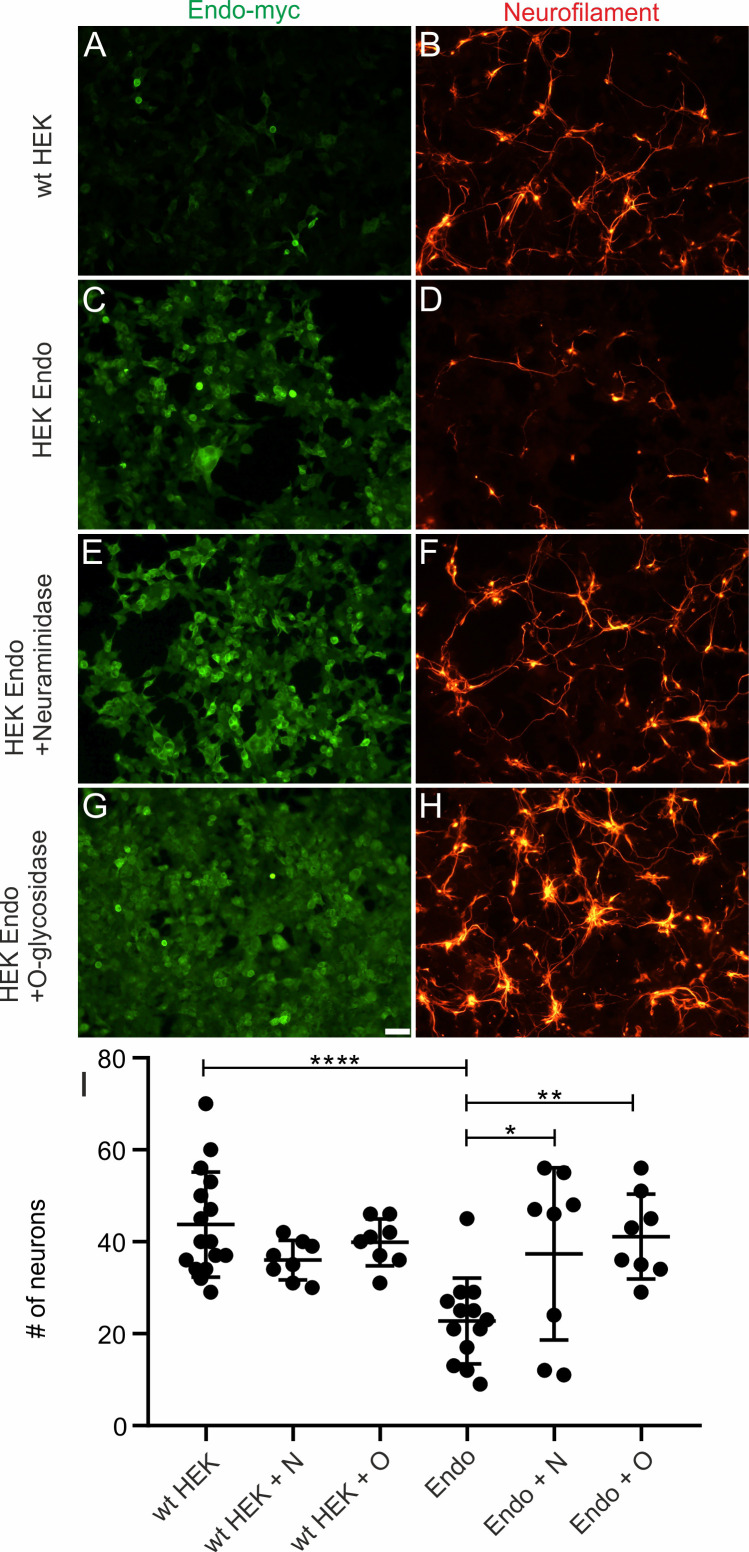
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Endoglycan expression reduces adhesion of motor neurons in vitro.