Figure 1:
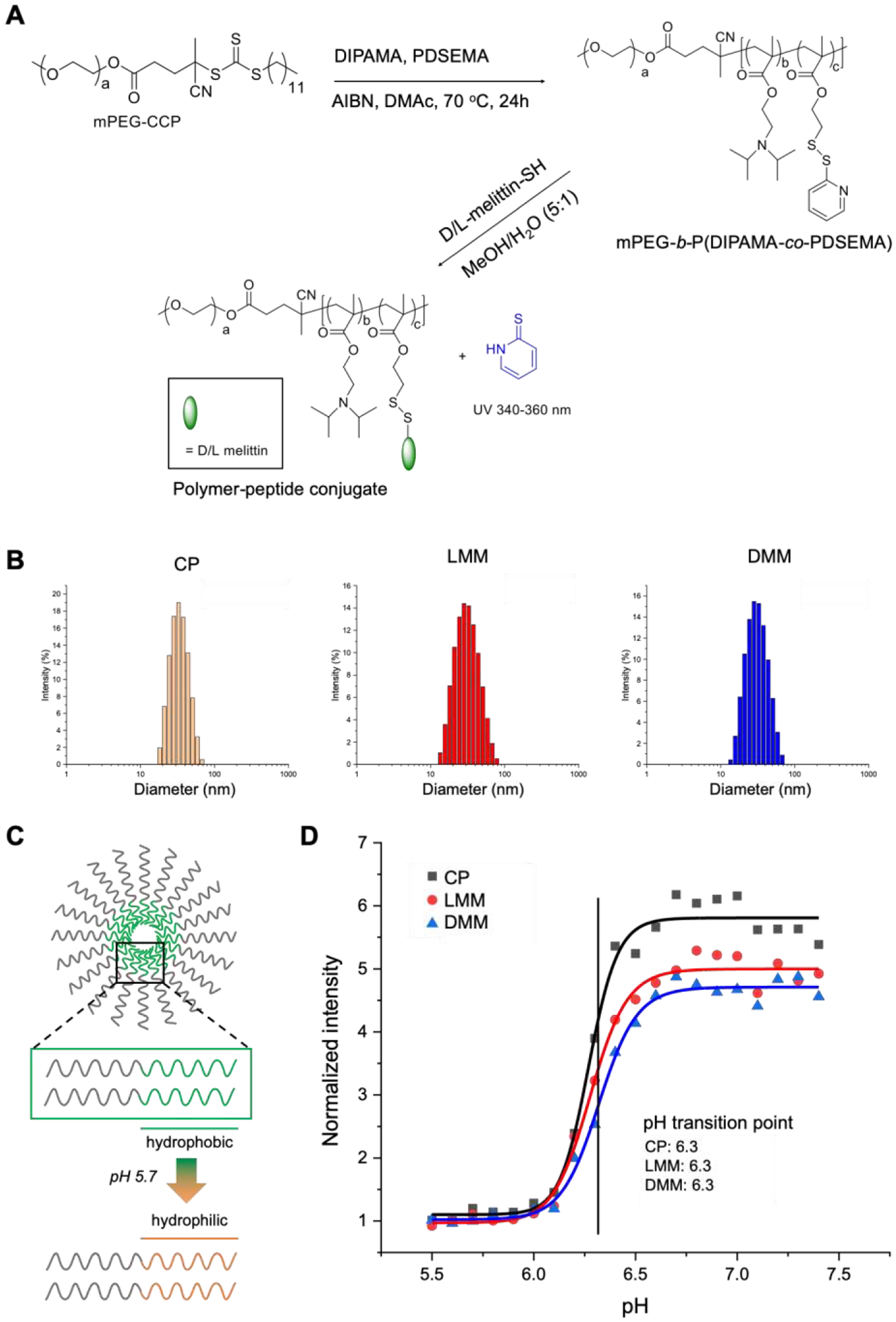
Polymer synthesis of micelles. A) Micelles were synthesized by RAFT polymerization of PEG, DIPAMA, and PDSEMA. L- or D-melittin was conjugated onto the polymer via disulfide exchange, yielding L-melittin micelles (LMM) or D-melittin micelles (DMM). Micelles without peptide are denoted as control polymer (CP). B) The hydrodynamic diameter of micelles were assessed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and was determined to be 34.6 ± 9.9, 32.9 ± 12.5, and 32.2 ± 11.0 nm for CP, LMM, and DMM, respectively. C) A schematic demonstrating the phase transition of DIPAMA, which switches from hydrophobic to hydrophilic at acidic pH. This enables pH-triggered display of melittin for endosomal escape. D) The transition point of micelles was determined to be pH 6.3 for CP, LMM, and DMM.
