Figure 5: NK cells produce IL-10 during sepsis in an IL-15-dependent manner.
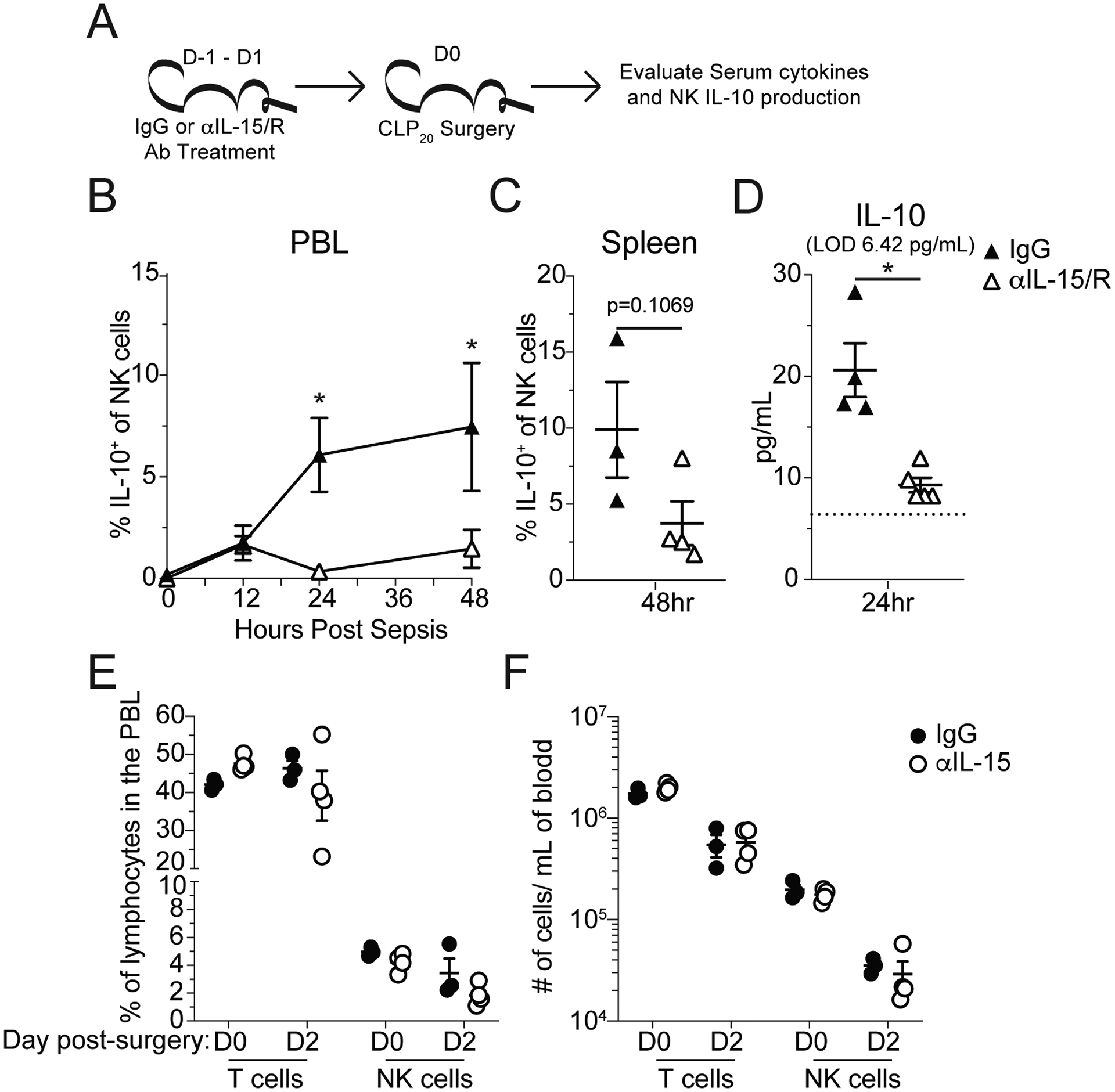
A) Experimental Design: Mice were given either control IgG or αIL-15/R blocking antibody, which inhibits both unbound, soluble IL-15 and IL-15 complexed with the IL-15 receptor alpha, 1 day prior to surgery and repeated on the day of sham or CLP20 surgery (Day 0) and Day 1 post-surgery. IL-10 production by NK cells and plasma IL-10 concentrations were monitored. (B) Frequency of IL-10-producing NK cells in the PBL of mice treated with either control IgG or αIL-15/R blocking antibody was assessed prior to and 12, 24, and 48hrs after surgery. (C) Frequency of IL-10-producing NK cells in the spleens of mice treated with either control IgG or αIL-15/R blocking antibody was assessed 48hrs after surgery. (D) Plasma IL-10 concentration of either control IgG or αIL-15/R blocking antibody treated mice 24hrs after surgery. Frequency (E) and number (F) of T cells and NK cells on the day of and 2 days after CLP20 surgery (1 and 3 days after initiation of IL-15 blockade, respectively). All data are representative from at least 2 independent experiments with at least 4–5 mice per group. * = p<0.05. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
