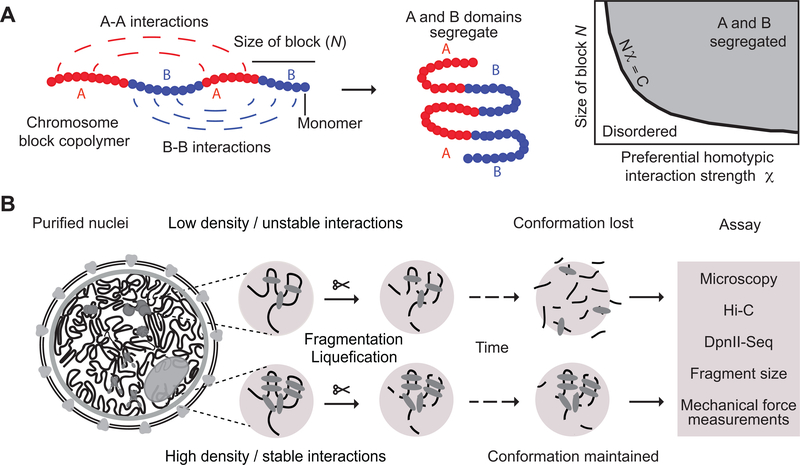
Fig. 1: Approach for measuring chromatin interaction stability.
A: Block copolymer composed of a series of alternating A and B blocks, each composed of a number of monomers (left). The polymer can fold into spatially segregated domains of As and Bs (middle). Flory-Huggins polymer theory predicts that spatial segregation will occur when the product of the length of the blocks N (the number of monomers that make up blocks) and their effective preferential homotypic interaction strength χ (difference in the strength of homotypic interactions as compared to heterotypic (A-B) interactions) is larger than a critical value C.
B: Workflow to determine the stability of chromatin interactions genome-wide. DNA: black, varying chromatin features or proteins maintaining DNA conformation: grey ovals.