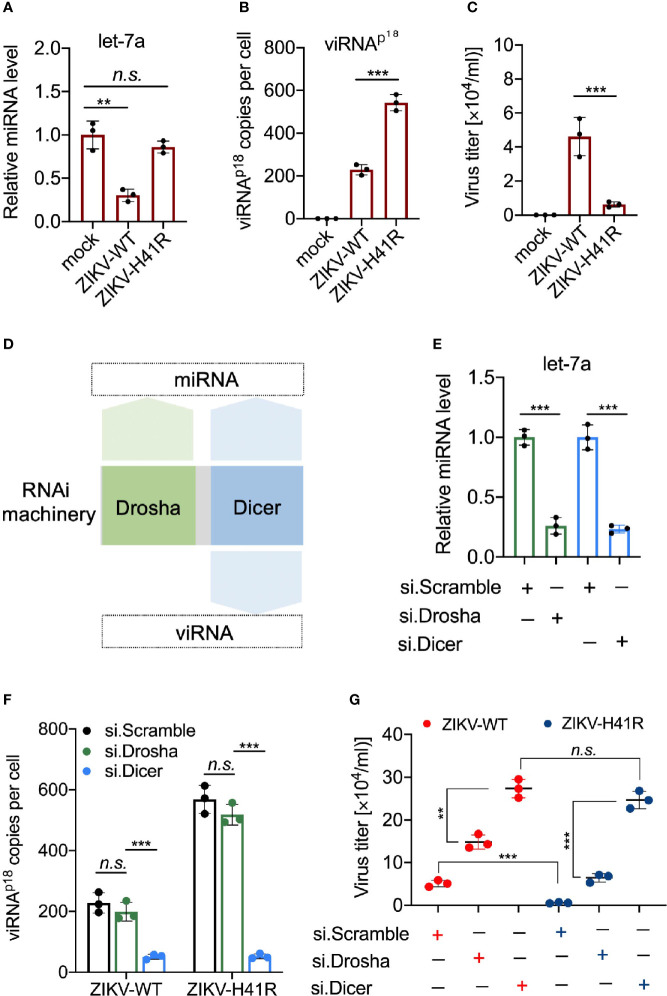
Figure 4.
Dicer-dependent viRNAs are potentially anti-viral in ZIKV-infected NSCs. (A) Taqman Advanced miRNA assays for miRNA let-7a in NSCs infected with ZIKV-WT or ZIKV-H41R. Mean ± SD; **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test. n.s., not significant. (B) Customed Taqman Advanced assays for viRNA-p18 (viRNAp18) detection in NSCs infected with ZIKV-WT or ZIKV-H41R. Mean ± SD; ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (C) NSCs were infection with ZIKV-WT or ZIKV-H41R mutant virus at MOI of 0.01, and culture supernatant were collected for virus titer determined by plaque assay. (D) Schematic diagram for the involvement of RNAi machinery components in miRNA or viRNA biogenesis. (E) Taqman Advanced miRNA assays for mature miRNA let-7a in scramble, Drosha, or Dicer siRNA-treated NSCs. Mean ± SD; ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t-test. (F) viRNA generation is dependent on Dicer function. 5x105 NSCs transfected with si.scramble, si.Drosha, or si.Dicer for 24 h were infected with ZIKV-WT or ZIKV-H41R at MOI of 0.1, and representative viRNAp18 expression was detected by customed TaqMan Advanced assays (see Materials and Methods). Mean ± SD; ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test. n.s., not significant. (G) Both miRNA and viRNA play important role to limit ZIKV replication in NSCs. 5 x105 NSCs were individually transfected with si.scramble, si.Dicer, or si.Drosha for 24 h, followed by infection with ZIKV-WT or ZIKV-H41R mutant virus at MOI of 0.01, and culture supernatant were collected for virus titer determined by plaque assay. Mean ± SD; **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t-test. n.s., not significant.