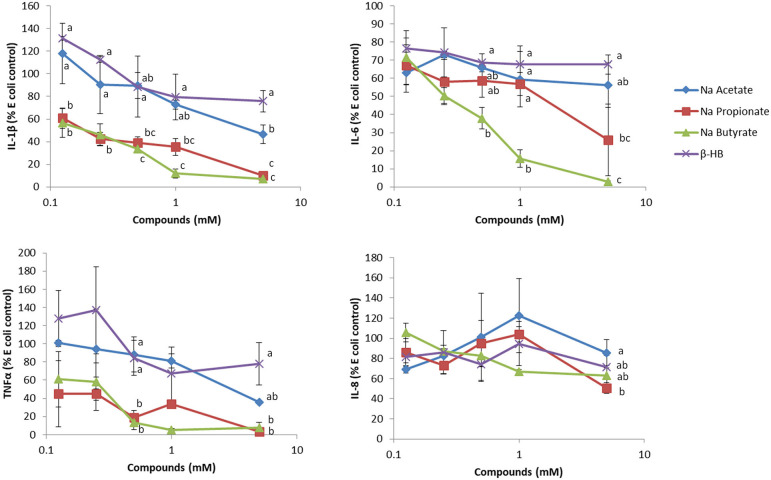
Figure 1.
The effect of sodium acetate, propionate, butyrate and β-hydroxybutyrate (β-HB) on E. coli-stimulated inflammatory cytokines from whole blood. Briefly, varying concentrations of SCFAs or β-HB dissolved in PBS were added to 50 μL whole blood, collected in sodium heparin glass tubes, for 15 min at 37°C, in a low (5%) oxygen incubator, and then challenged with Escherichia coli (One Shot INV 110, Life Technologies, Burlington, ON) at a final concentration of 2 × 104 cells/mL for 7 h as previously described (94). PBS (100 μL) was added to the whole blood, mixed well and upon centrifugation at 424 × g at 4°C for 5 min in an Allegra X-12R centrifuge, the plasma was recovered for ELISA analysis (n = 3). This experiment was repeated two additional times, and results shown are representative of three independent experiments. Results are expressed as percentages, relative to E.coli-stimulated cells. The effect of the sodium acetate, butyrate, propionate and β-HB at each concentration on the cytokine/chemokine level was evaluated using one way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison post-hoc analysis. The different letters denote significant (P < 0.05) differences between treatments at the same concentration. Experiments using blood collected from human subjects were reviewed and approved by the joint Clinical Research Ethics Board of the University of British Columbia and the BC Cancer (#H12–00727).