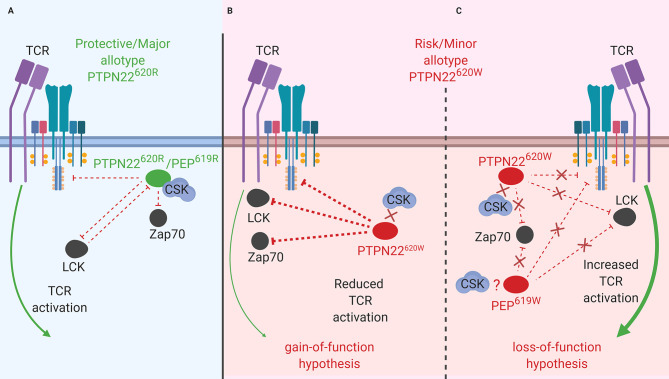
Figure 1.
PTPN22 function in T cells. (A) PTPN22620R and PEP619R are negative regulators of TCR signaling in T cells where they dephosphorylate/deactivate signaling intermediates and reduce signaling from the TCR to the nucleus. (B) The PTPN22620W gain-of-function hypothesis. In this scenario, PTPN22620W is more active and dephosphorylates signaling intermediates at an increased rate compared to PTPN22620R. This blunts TCR signaling compared to PTPN22620R and reduces T cell response. (C) The PTPN22620W and PEP619W loss-of-function hypothesis. In this scenario, PTPN22620W/PEP619W are less efficient at dephosphorylating TCR signaling intermediates compared to PTPN22620R/PEP619R. This allows more signal from the TCR to reach the nucleus and increases T cell response to TCR stimulation.