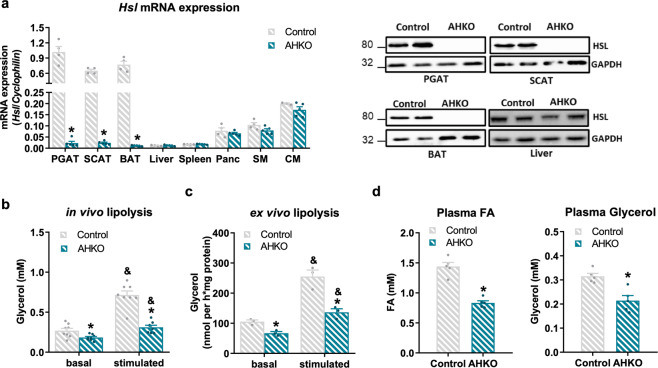
Fig. 1. Effects of adipocyte-specific HSL deletion on adipocyte lipolysis.
a Left: Hsl mRNA expression relative to Cyclophilin reference gene by qPCR in adipose tissue (PGAT perigonadal, SCAT subcutaneous, BAT brown) and non-adipose tissue (Panc pancreas, SM skeletal muscle [quadriceps], CM cardiac muscle) with Hsl expression in control PGAT arbitrarily set to 1. Right: HSL protein expression in adipose tissue and liver (M, 33 weeks, chow, 12 h fasted, n = 4–5 animals/genotype). b In vivo lipolysis determined by plasma glycerol levels before (basal) and 15 min (stimulated) after ip administration of 1 mg kg−1 body weight of the β3-adrenergic receptor agonist CL-316,243 (M, 10 weeks, chow, 6 h fasted, n = 8 animals/genotype). c Ex vivo lipolysis determined by glycerol released from PGAT explants incubated without (basal) and with (stimulated) 10 µM isoproterenol for 1 h (M, 12 weeks, chow, ad libitum fed, n = 3 animals/genotype). d Plasma fatty acid (FA; left) and glycerol levels (right) (M, 26 weeks, chow, 12 h fasted, n = 5 animals/genotype). Data represent mean + SEM. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s two-tailed t test. P < 0.05: * for effect of genotype; & for effect of treatment.