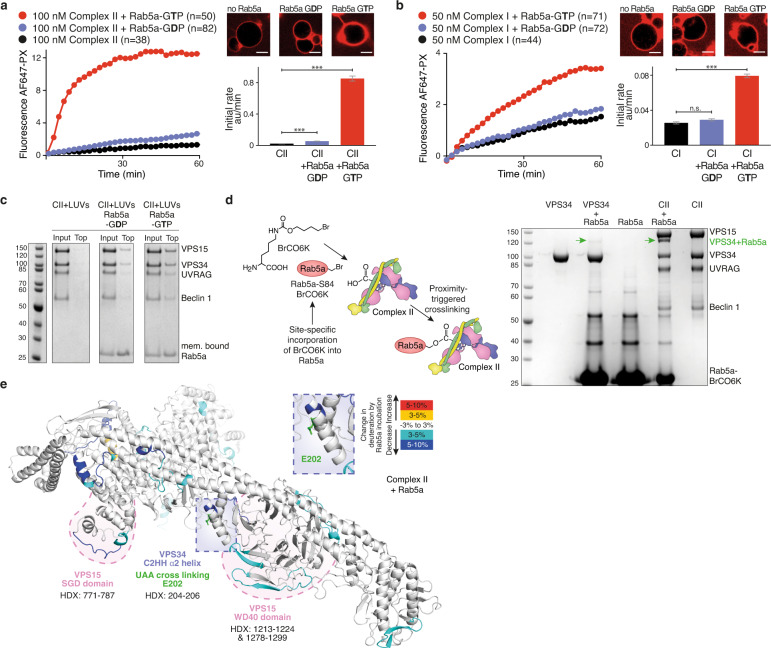
Fig. 1. Membrane-bound Rab5a–GTP recruits and activates VPS34 complex II.
a, b GUV-based activity with membrane-tethered Rab5a. The reaction progress curves and initial rates are shown. Micrographs: AF647-PX signals at the end of reactions. Scale bars: 5 μm. Bar graphs: initial rates of the reaction curves (AF647-PX fluorescence change/min in arbitrary units, AU). a Complex II is greatly activated by membrane-tethered Rab5a in a GTP-dependent manner. b Complex I is only modestly activated by membrane-attached Rab5a–GTP. c Complex II is recruited to Rab5a-decorated LUVs in a GTP-dependent manner as measured by a flotation assay. Here, complex II is mixed with LUVs and the mixture is added on top of a sucrose gradient and centrifuged. Membrane-bound proteins float up to the top of the gradient as seen in gel lanes (Top). Gel quantification can be found in Supplementary Fig. 2a. d Mapping the Rab5a–GTP binding site by proximity-triggered crosslinking of complex II. SDS-PAGE gel of crosslinking reactions, products indicated by green arrows. e Mapping the Rab5a binding site on complex II by the HDX-MS. HDX changes are displayed on a model of human complex II created with PyMOL. Rab5a binding protects (coloured in cyan and blue) the VPS34 C2 helical hairpin insertion (C2HH) and the VPS15 SGD and WD40 domains. The VPS34 C2 (E202) that is crosslinked by unnatural amino acid Rab5a-84BrCO6K is coloured green and shown in an expanded panel. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.