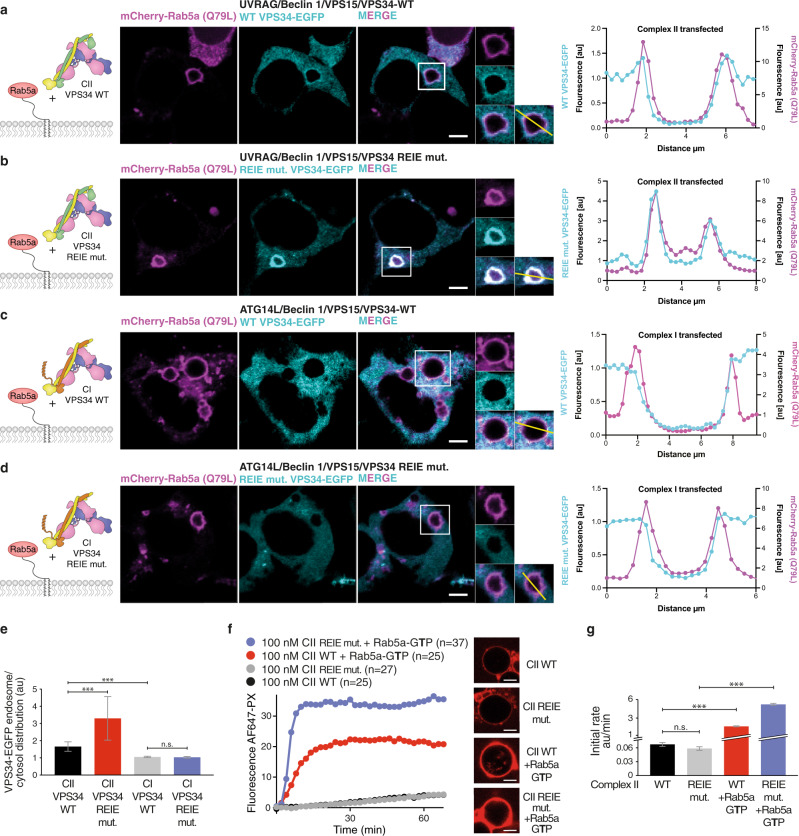
Fig. 2. The C2 helical insertion (C2HH) of VPS34 is a critical element for the interaction of complex II with Rab5a.
a, b GTP-locked Rab5a (Q79L) and all four components of complex II, containing either C-terminally EGFP-tagged WT (a) or C2HH mutant REIE > AAAA VPS34 (b), were coexpressed in HEK293T cells. Confocal images show cellular localisation of mCherry–Rab5a-Q79L (magenta) and VPS34-EGFP (cyan). To the right of each panel, traces for the fluorescence along the transect indicated by the line in the micrograph are shown. The C2HH REIE mutant markedly increased colocalization of complex II with Rab5a (b, e) compared to VPS34 WT (a, e). c, d GTP-locked Rab5a (Q79L) and all four components of complex I, containing either C-terminally EGFP-tagged WT (c) or mutant REIE > AAAA VPS34 (d), were coexpressed in HEK293T cells. The mutant had no impact on the colocalization of complex I with Rab5a (c–e), quantitated as described in methods. Error bars: standard deviation. ***: p < 0.0001; n.s.: p > 0.05. Scale bars: 10 μm. f GUV assay of activity of complex II shows that the VPS34 C2HH REIE > AAAA mutation greatly potentiates the activation of complex II by Rab5a–GTP, without affecting the basal activity of complex II. Micrographs: AF647-PX signals at the end of reactions. Scale bars: 5 μm. g The initial rates in the GUV assay in f (AF647-PX fluorescence change/min in arbitrary units, AU) are depicted. ***: p < 0.001; n.s.: p > 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.